|
Prof. Dr. Satya Subrahmanyam Department of Business and Management TISHK International University Erbil, Kurdistan Satya.sub@ishik@edu.iq |
Zhalla Farwq Hamadamin Department of Business and Management TISHK International University Erbil, Kurdistan |
The purpose of this research paper is to examine therole of supportive organizational culture in private hospitals to understand the effect and relationship between the hospital’s supportive culture and strategic success in Erbil city, whereasusing a qualitative method for a framework in thepaper.So, examined the impact of organizational supportive culture dimensions on the strategic success that will increase the understanding of theessential characteristics of supportive culture particularly in private hospitals. The paper also employed a survey questionnaire as a data collection instrument — the survey based on a random sample of 30health staffs. Nevertheless, two private hospitals operating in Erbil, selected due to a commitment to culture and strategy, besides having high health services performance. The statistical program SPSS-24 used in the processing and analysis of the data. As a result, this research paper found that there is a significant positive relationship between supportive organizational culture and strategic success. Moreover, the results of the regression analysis displayed thatorganizational culture effect strategic success. The paper finding also provides insight into the impact of hospital culture in improving hospital framework to enable operational, strategic success.
Keywords: Organizational Culture, Cultural Values, Cultural Teamwork, Culture of Communication, and Strategic Success
This research paper aimed at examining the role of organizational culture on strategic success in private hospitals. Regarding organizational culture, there are common beliefs in the minds of members of the organization about how to encourage individual initiatives, the availability of original conditions, the degree of risk acceptance, achievement and high performance, and the focus on results regard the hospital’s strategic success. While all these mentioned have a unified culture that contributes in one way or another to increase the effectiveness of the organization. Organizational culture, therefore, influences the behaviour of staffs as employees act by the values and beliefs of the organization that express how the business performed. Many business organizations are becoming interested in the organization's culture and giving it a priority in study and analysis because they include structural and behavioural dimensions. The workers accept the more common values and beliefs, and they are consistent with their values and beliefs, it is an indication of the strength of the culture and the extent of its influence. In recent years, the subject of culture and strategy has received the attention of researchers and scholars in all areas of management, because it is of great importance in influencing the behaviour of employees and thus in the performance of the organization. While organizational culture has received increasing attention from business organizations, organizational culture also plays a vital role in realizing the plans and strategies success applied during change processes in the organization in order to achieve its objectives and ensure its sustainability and continuity. Through organizational culture differ from each other regarding the fundamental characteristics that govern the way of work, each organization has its own culture as an identity, which differs from the others. The existence of a distinct organizational culture for the organization contributes to the consolidation of unified thinking for its members and helps to establish common principles for decision-making. Organizational managers recognize that culture and strategy affect staff behaviour and practices that should be consistent with prevailing organizational beliefs about the organization's core characteristics of continuity.
The problem of the research embodied in several ways, including theory, researchers need to explore concepts, approaches, perspectives, measurements. Besides what is the nature of the relationship between organizational culture and strategic success? Thus, creating a framework for this topic, which is still lacking in theoretical administrative literature. As well as how to measure organizational culture as an intangible asset, and strategic success across their various indicators, not only to mention the relationship between variables, if any, and the extent to which the independent variable organizational culture. While private hospitals in Erbil mostly face varying degrees of ambiguity in the surrounding environment such as the economic, social, technological, and competitive environment, and the instructions of the ministry of health. Private hospitals in Erbil also faced the consequences of change in the environment and the problems of uncertainty, which affected the formation of their culture and strategic success.
The primary purpose of this research paper is to examine the role of supportive organizational culture on strategic success in private hospitals to understand the effect and relationship between the hospital’s supportive culture and strategic success in Erbil city.
To analyze the significance of culture and strategy in private hospitals. To examine the relationship between the supportive organizational cultureand private hospital strategic success in Erbil city. To examining the supportive organizational culture and its influence effect on strategic success in Erbil city.
This research paper efforts to answer one essential question: To what extent does the supportive organizational culture effect on strategic success? Hence, to answer this question, this paper addresses the following sub-questions:
1. What are the primary dimensions of organizational culture? 2. Do organizational culture dimensions display significant sequential reliability? 3. Do organizational culture dimensions differ in their comparative significance across private hospitals in Erbil? 4. Are organizational culture dimensions significantly related to strategic success? 5. What are the effects of organizational culture on strategic success?
Based on the literature reviewed that related to this research paper’s variables organizational culture and strategic success, a conceptual scheme established. While bearing in mind the purpose of the paper is to examine the role of organizational culture in the strategic success that affords a conceptualization of the basic model linked to the topic of the paper. The conceptual scheme and hypotheses are also explaining the relationship and effect between these research variables, as shown in Figure 1.
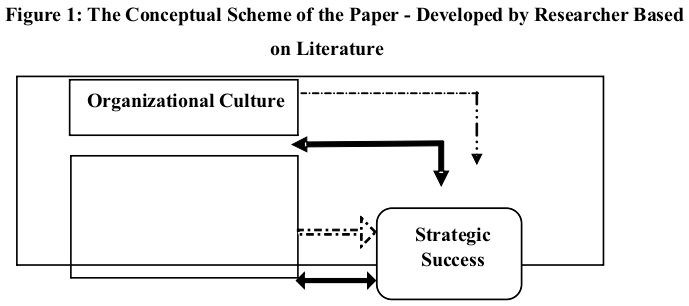
Theoretically, this research paper established on the attitude that supportive organizational culture (cultural values, teamwork, communication, and support and motivation), have relationship effect in the strategic success of the private hospitals. Thus, the paper pursues to test the following hypothesis:
First main hypothesis H1: There is a positive relationship between supportive organizational culture and strategic success of the private hospitals operating in Erbil city, at the level of (0 ≤ 0.05) H1.1: There is a positive relationship between cultural values and the strategic success of the private hospitalsin Erbil city. H1.2: There is a positive relationship between teamwork and strategic success of the private hospitals in Erbil city. H1.3: There is a positive relationship between communication and strategic success of the private hospitals in Erbil city. H1.4: There is a positive relationship between support and motivation and strategic success of the private hospitals in Erbil city.
Second main hypothesis H2: There is a positive effect of the supportive organizational culture in the strategic success of the private hospitals operating in Erbil city, at the level of (0 ≤ 0.05) H2.1: There is a positive effect of the cultural values in the strategic success of the private hospitalsin Erbil city. H2.2: There is a positive effect of the teamwork in the strategic success of the private hospitals in Erbil city. H2.3: There is a positive effect of communication in the strategic success of the private hospitals in Erbil city. H2.4: There is a positive effect of the support and motivation in the strategic success of the private hospitals in Erbil city.
There are diverse definitions of organizational culture regarding the different views of researchers and the conditions in which each country lives. Besides each researcher defines it according to its point of view. According to MacIntosh and Doherty (2010:108), organizational culture is a set of shared values, beliefs, philosophies, and other components that are created between individuals in a way that suits their working and communication relationships, encouraging the need to cooperate and with management to avoid regulatory processes. During negotiations and ongoing practices among group members becomes a source of the signal of what is acceptable or unacceptable to the organization concerning right and wrong conduct. Organizational culture is a complex set of values, beliefs, abstractions, and symbols that define the way for the organization to operate (Cheung, 2011: 34). According to Khamis (2012: 212), the organization provides trust, equality, cooperation and a focus on the human aspect in this environment. While there are those, who believe that the supportive organizational culture has two basic types: Which is spread throughout the organization and is trusted and accepted by all members of the organization who share a homogeneous set of values, beliefs, traditions, and standards that govern their conduct within the organization, it is a strong link between the organization's elements and helps to channel its energy into productive actions that enable it to respond quickly and appropriate to the needs of its clients and to ask individuals involved in it, which helps the organization to achieve its objectives and strategic success.(Naranjoet al., 2011). While, Mansor and Tayib (2010: 84) supportive culture are the basic principles invented or discovered by a particular group, with the aim of getting used to solving specific problems regarding adapting to their external surroundings, harmony or internal integration. These basic principles are taught to each in the group as the best and most appropriate way of thinking and feeling the problems related to work collective. Organizational culture is enhancing internal integration between the organization's resources through communication and working together effectively. Also, achieving adaptation among employees in the organization and the relevant external environment (Khamis, 2012).
According to Baird et al., (2007) strategic success is the most significant strategic decision whose effect on the organizational operations of a firm is crucial. The concept of corporation management using strategy represents an essential way of achieving the goals of an organization. The concept of strategic success has assumed a significant place in some studies and research, where its concepts have evolved by the organizational thought that preceded it with the concepts of efficiency and effectiveness. It is survival, adaptation, and growth regardless of the objectives achieved. The entry of the organization in the measure of effectiveness indicated the survival criterion as a final measure of effectiveness (Habtoor, 2006).According to Baird et al., (2007) the strategic success can achieve through organizational culture in two fundamental ways. First, in formulating a strategy, the organization’s management must take into account the assumptions, values and cultural norms that it must provide in advance for the new strategy to comply with them. In order to be able to do so, at the stage of strategic analysis, management must conduct and examine the organizational cultural appearance. Also, the management, in the strategy selection phase, must be prepared to adapt the strategy to the organization's current culture. Gupta (2011) on the other hand, if the administration is forced to choose a strategy that does not conform to the existing culture, it must be ready and able to fill the 'cultural gap' during the implementation of the strategy, which achieved by changing the existing culture. In order to do this, management must have the capabilities and know how to change organizational culture in a planned way.
The empirical researches, in addition to its general details, indicates that supportive organizational culture and strategic success are related and that their agreement and compatibility are an advantage for the organization (Alvesson,2002).Organizational culture affects strategy in both the drafting process, as well as in the process of implementation — organizational culture affects the formulation of strategy through the formation of schemes and interpretative meanings, which are appointed by strategic decision makers of the facts inside and outside the company (Baird et al., 2007). The culture determines how senior management gathers information, how it views and interprets the environment and the organization's resources, but also illustrates how strategic decisions are taken, that is, making the strategy choice - the organization's culture strategy - by legitimizing the strategy or delegitimizing it consistency between selected cultural values and strategy. When a strategic culture begins, it greatly facilitates the implementation of the strategy. When culture takes away the legitimacy of strategy in the eyes of staff and managers, it implements the chosen strategy impossible (Chow and Liu, 2009). According to Gupta (2011) a strategy in organizational culture through the institutionalization or exclusion of culture, based on compatibility with cultural values and norms. If the activities through which the specific strategy formulated and implemented are consistent with cultural values and norms, the strategy will institutionalize and strengthen the existing culture. Yarbrough et al., (2011) on the contrary, the long-term and consistent implementation of the chosen strategy will eliminate the organizational culture, where the process of strategic success begins. The primary management recommendation regarding the relationship between strategy and organizational culture is that a way must be found for the organization's core management components (Ashkanasy et al., 2000).
The purpose of the methodology section used in this research paper is to reach its purpose that is to examines the role of supportive organizational culture in strategic success: research in private hospitals in Erbil city. While the nature of this paper involves both qualitative and quantitative method, quantitative method is used for analyzing numerical data while the survey design allows collecting data using questionnaires.
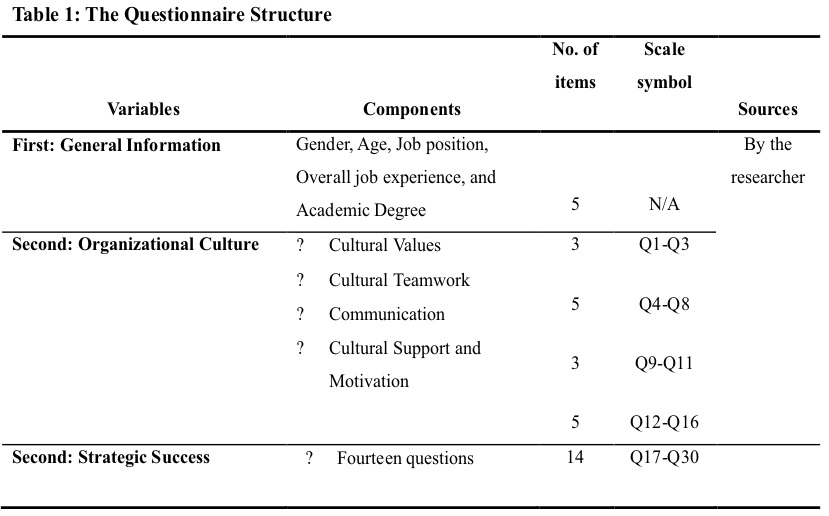
To obtain the required data for the research variables, the researcher gathered the primary data and information by conducting the survey. Correspondingly, to make the survey useful, a questionnaire scale established reliant on the literature reviewed. Also, the questionnaire self-designed as a vital data collection technique. Nevertheless, the secondary data gathered by studying and citing the literature available that interrelated to culture and strategy, specifically researches, journals, thesis, and related books. As shown in Table 1, below and previously mentioned that this research paper used a questionnaire form to collect data and planned it in a scale comprised of the closed-ended type of statements. So, the closed-ended statements or questions meant to obtain accurate evidence as well as to measure the health staff’s perspectives. Thus, the questionnaire divided into three parts first part includes five demographic variables, while the second and third parts include questions on the research topics, as revealed through appendix 1.
The sampling process in this research paper purpose is to narrow down the research population to establish a proper sample where linked data needed to comprise the paper purpose. The data have taken from 30 respondents of private hospitals in Erbil. Mostly those who are relevant to the research topic regarding knowledge and profession, where (35) questionnaire forms distributed among survey sample who freely accept the invitation to participate to the survey by responding to the questions. So, the response rate was (85.14%), nevertheless, five questionnaires invalid and taken out from the sample size which launches as the research sample.
This purpose of this section of the paper is to determine the data analysis and findings that begging with a description of the demographic variables, collected from the respondents the private hospital managements in Erbil city. The demographic variables comprise frequency distributions. Though, the second part of this sections hows the statistical results of the data analysis
The demographic variables were composed and explained to provide a close image of the survey sampling. As revealed in Table2, the private hospital male managers who freely participated in this survey came at the rate 56.66% of the total survey sample, or (17) managers, although, private hospital’s female managers came at the rate 43.34% or (13) female participators. While the percentage and frequency of participators age groups showed that 33.3% or (10) person aged between 35-44 years old Though 30% or (9) survey respondents aged 55-64.26.67% or (8) person of the total survey sample aged 45 to 54 years. Lastly, the managers who aged between 25-34 years old, participated in this survey came at last 10% or (3) managers only. Hence, it stated that most private hospital managers in Erbil are young and in the middle ages. It can realize in a table below that the percentage and frequency of the survey sample job position, most managers who partook in the survey were in the department manager, and came at a rate of 56.6% or (17) individuals. More, 33.33% or (10) of the total research sample were at the position of administrative managers while hospital managers at a rate of 10% or (3) managers. Table 2, shows that most private hospital’s managers who contributed in the survey their overall job healthcare experience are between 21-30 years, at the rate of 33.3%, or (10) person of the overall survey sample. Furthermore, from 31-40 years came at a rate of 26.6% or (8) individuals. While23.3% or (7) persons' job practiced are between 11-20 years. Also, 10% of the whole research sample experienced between 1-10. Though, the percentage and frequency of the survey sample academic degree, 56.67% or (17) person are master degree holders, where 33.3% or (10) contributors in private hospitals hold bachelor degrees. Also, Ph.D. or board comes at 10%. So, it means the most private hospital’s managers who contributed to this survey high university certificates holders.

The value of Cronbach’s alpha for overall organizational culture indicators is (0.901>0.60), besides values of its dimensions namely: cultural values, teamwork, communication, support and motivation, and strategic success are (0.714, 0.806, 0.811, and 0.828) respectively, so, all the values bigger than 0.60. While, the Cronbach’s alpha value of strategic success indicators is (0.903>0.60), which showed a high level of reliability in the whole set of items the overall values (0.905>0.60). Therefore, the survey questionnaire employed for data gathering restrained highly reliable, as revealed in a table below 3.
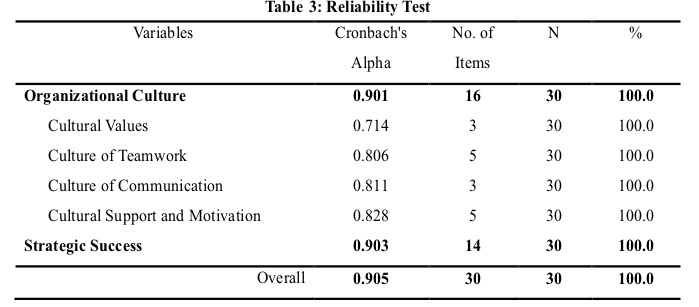
Table 4, shows the statistical results of mean and standard deviation for the independent variable organizational culture is (4.110, and 0.473) respectively. The weight of agreement is 82.2% of the total replies specified that organizational culture as an independent research variable significant for strategic organizational success; which supported by t-test (81.715) df (29) at the Sig (0.000<0.05). While, the values of statistical means of the hospital's culture dimensions namely; cultural values, teamwork, communication, and support and motivation are (4.002, 4.103, 4.108, and 4.102) respectively, and standard deviation scores for those dimensions are (0.502, 0.613, 0.537, and 0.580) respectively. Although (80.04%, 82.06%, 82.16%, and 82.04%) respectively of the overall answers agreed on the significance of the culture dimensions, i.e., cultural values, teamwork, communication, and support and motivation, that supported by t-test (82.097, 78.401, 77.789, and 70.550) respectively at the p-values (0.000, 0.000, 0.000, and 0.000) respectively, which all less than alpha 0.05, therefore, all the dimensions significant (p-value<0.05). As realized fromtable4, the result of statistical mean and standard deviation values for strategic success is (3.880, and 0.668) respectively. However, 83.3% of the total responses agreed on the importance of strategic success as the dependent variable. So, the overall t-test (81.257), p-value (0.000), is less than alpha 0.05. Thus, strategic success significant (p-value<0.05).Accordingly, the above results confirm the influence of organizational culture and its dimensions on strategic success.

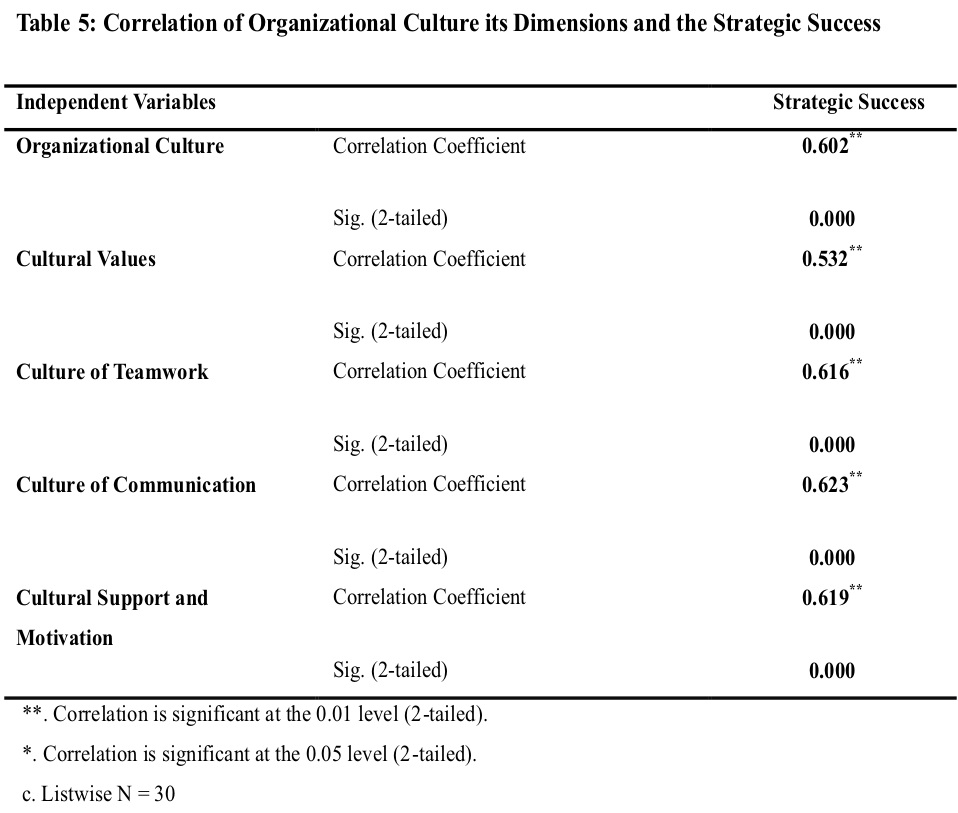
As revealed in table5, the correlation test results confirm that independent variables correlated to the dependent variable, p-values less than alpha (p<0.05). So, the organizational culture significantly correlated with strategic success (r= 0.602**; p0.000<0.05). Correspondingly, the hospital's culture dimensions namely; cultural values, teamwork, communication, support, and motivation positively correlated with strategic success. Table 5, also explains that the communication, teamwork, and support and motivation through (r=0.623**, 0.619**, and 0.616**) respectively, have strong positive relationships with strategic success, where a p-value of (0.000, 0.000 and 0.000) respectively. While the cultural values have the weakest relationship with strategic success, compare to the other three dimensions. Hence, the null hypotheses rejected, and the alternatives (H1, H1.1, H1.2, H1.3, and H1.4,) accepted.
As shown in table6, a multiple and simple linear regression established to examine the effect of the organizational culture on strategic success. So, the model summary showed in the table below that the coefficient of determination R Square is (0.386) which demonstrates that the variation clarified the dependent variable due to independent variables. Thus, this confirms the culture dimensions namely; cultural values, teamwork, communication, support and motivation analyses for 38.6% of the private hospitals in Erbil.
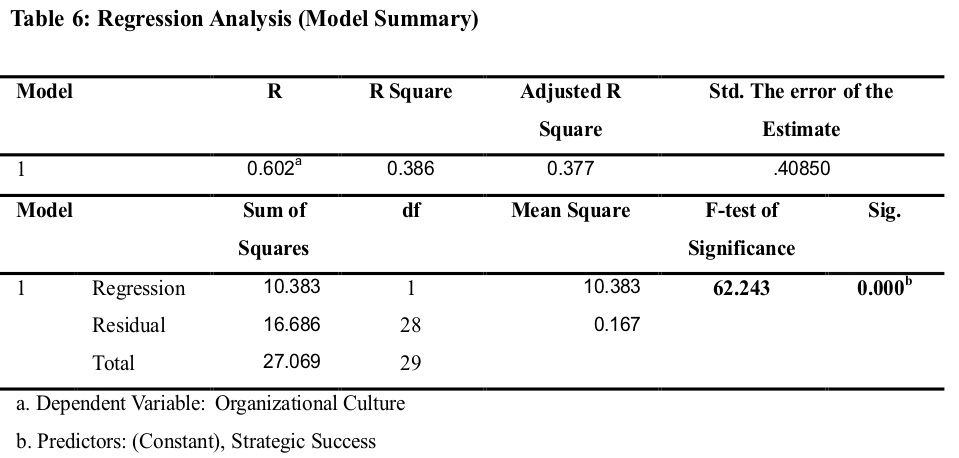
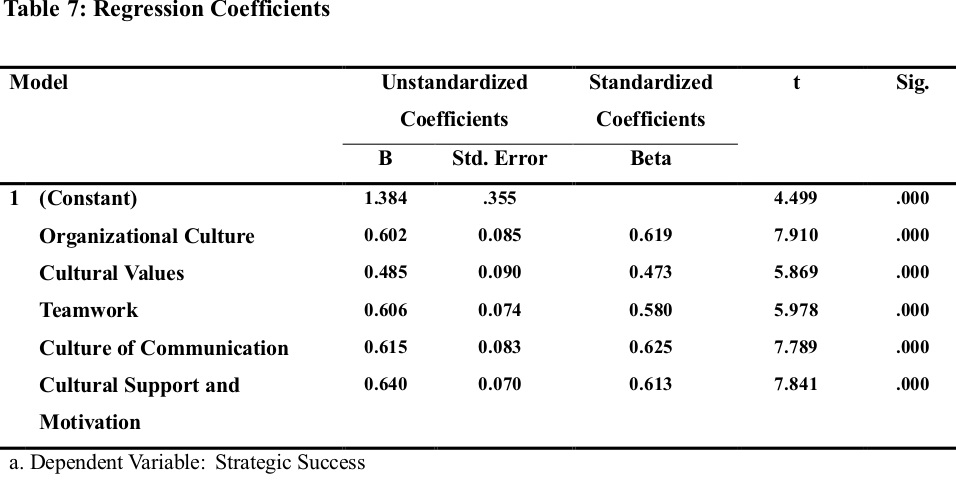
Table 6, presented F-test of significance, where F (62.243) informs significant (p0.00< 0.05) and appropriateness of the proposed model,thus, the model has it is statistical significance in valuing how the organizational culture effect on Strategic Success. Hence, null hypotheses rejected, and the alternative hypotheses (H2) accepted.As the results revealed in table 7, statistically there is a significant effect of the organizational culture dimensions on the strategic success of the private hospitals in Erbil city. As well-defined by an extent of B (0.619, 0.473, 0.580, 0.625, and 0.613) respectively for the hospital's organizational culture, cultural values, teamwork, communication, support and motivation, and as confirmsby p-values (0.000, 0.000, 0.000, and 0.000) respectively.Also, the t-test = (7.910; p<0.05) for supportive organizationalculture as an independent variable, it means significant and support the results. So, the t= (5.869, 5.978, 7.789, 7.789, and 7.841) for its dimensions respectively, the high effects of the hospital's communication, support and motivation and, teamwork, while the lower one was the cultural values between dimensions of organizational culture.Hence, null hypotheses rejected and alternative hypotheses as (H2.1, H2.2, H2.3,and H2.4) accepted.
This research paper is carried out to examine the role of supportive organizational culture on strategic success. Subsequently, to reach the purpose of the paper, the researcher examined the relationship between supportive organizational culture and the strategic success process by analyzing the survey sample perspectives from the private hospitals in Erbil. Thus, the researcher captivated the effect of supportive organizational culture in this relationship. Based on the findings of the descriptive analysis, that it can predict the supportive organizational culture and its dimensions exercise significant effects on the strategic success according to the survey sample’s viewpoints, accordingly, there are good levels of supportive organizational culture in surveyed hospitals in Erbil. Also, the outcomes clarified that communication, support and motivation, and teamwork riches the highest rate among the other four dimensions. Though the findings also revealed that a positive and significant relationship occurs between supportive organizational culture and strategic success besides, communication, support and motivation, and teamwork reached the most substantial positive relationship with the strategic success. Furthermore, the results of regression analysis established that statistically, the supportive organizational culture has effect in the strategic success, Nevertheless, organizational culture communication, support and motivation, and teamwork have the most potent effect on the strategic success.
For the private hospitals in Erbil to have active culture and strategic success, as well as healthcare services growth, and reliability, hospital managers should train to improve supportive organizational culture and its dimensions as organizational values, teamwork, communication, and support and motivation, that will approve the success of the hospital’s strategy. Thus, it is important to practice an effective strategic formulation, its implementation and keep high levels of its dimensions, Though, increasing consideration in the search for some new ways to achieve the success of the hospital’s strategy.
This research was supported by TISHK International University. I thank Dr. Fatih Cura, Dean of The Faculty of Administrative Sciences and Economics and Mr. Karwan Hushyar, Head of Business & Management Department who provided insight and expertise that greatly assisted the research, although they may not agree with all of the interpretations/conclusions of this paper. Nobody has been more important to me in the pursuit of this project than the members of my family. I would like to thank my parents; whose love and guidance are with me in whatever I pursue. They are the ultimate role models. Most importantly, I wish to thank my loving and supportive wife, Ms. Kumari, and my only wonderful daughter, Ms. Gnana Satya Sri, who provide unending inspiration.
Alvesson, M. (2002). Understanding Organizational Culture.London: Sage. Ashkanasy, N., Wilderom, C., and Peterson, M. (2000). Handbookof Organizational Culture and Climate. Thousand Oaks: Sage. Baird, K., Harrison G., and Reeve R. (2007). The Culture of AustralianOrganizations andits Relation With Strategy, InternationalJournal of Business Studies, Vol. (15), No. (1), pp.15- 41. Cheung, S. O. (2011). Towards an Organizational Culture Framework in Construction, International Journal of Project Management, Vol. (29), pp.32-43. Chow, I.H.S., and Liu S.S. (2009). The Effect of Aligning OrganizationalCulture and Business Strategy With HR Systems on FirmPerformance In Chinese Enterprises, The International Journal ofHuman Resource Management, Vol. (20), No. (11), pp. 2292–2310. MacIntosh, W. Eric, and Doherty, Alison. (2010). The Influence of Organizational Culture on Job Satisfaction AndIntention To Leave,Sports Management Review, Vol (13), ), No (2), pp.101-116. Gupta, B. (2011). A Comparative Study of Organizational Strategyand Culture Across Industry, Benchmarking: An InternationalJournal, Vol. (18), No. (4), pp. 510-528. Habtoor, A. S. (2006). Strategic Management: New Management in a Changing World, First Edition. Dar Wael, Amman, Jordan. Khamis, N.M. (2012). The Effect of Organizational Culture on Adopting Environmental Management System, ISO 14001 Journal of Anbar University for Economic and Administrative Sciences, Vol. (4), No. (8), pp.201-220. Mansor, M., and Tayib, M. (2010). An Empirical Examination of Organizational Culture, Job Stress and Job Satisfaction within the Indirect Tax Administration in Malaysia, International Journal of Business and Social Science, Vol (1), No (1), pp.80-91. Naranjo-Valencia J.C., Jimenez-Jimenez D., and Sanz-Valle R. (2011). Innovation or Imitation? The Role of Organizational Culture, Management Decision, Vol. (49), No. (1), pp.55–72. Yarbrough L., Morgan N.A., and Vorhies D.W. (2011).The Impact of Product Market Strategy-Organizational Culture F T On Business Performance, Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, Vol. (39), pp. 555–573.