|
S. Lakshmi Research Scholar Research and development centre Bharathiar University, Coimbatore |
Dr. V. Kavida Associate professor Pondicherry University Puducherry, India |
From a child to adult everyone is interested in watching television. Most of our leisure hours are spent on watching TV. Every household whether lower income group or middle-income group of higher income group every one possesses television. Earlier days television was thought as luxury goods but not anymore today it is an absolute necessity . Brand trust is the willingness of the buyer to repetitively purchase a same product again and again. Purchase intention is the idea a customer is having to purchase a particular brand. The present study aims to study the effects of brand trust on purchase intentions of television with reference to Chennai city. Data was collected from 650 respondents through questionnaire and the data were analysed using SPSS tools. The result obtained is that brand trust has an impact on purchase intentions of television.
Key Words : Brand Trust, Purchase Intentions, Television.
From a child to adult everyone is interested in watching television. Most of our leisure hours are spent on watching TV. Every household whether lower income group or middle-income group of higher income group every one possesses television. Earlier days television was thought as luxury goods but not anymore today it is an absolute necessity. All the current events and news we get it through television. In earlier days, there were only some brands of television. Today we have number of manufacturers who sell television. The brands that are chosen for study are Samsung, LG, Sony, Videocon and others.
Brand Trust:
Chaudhuri and Hol- brook (2001) define brand trust as “the willingness of the average consumer to rely on the ability of thebrand to perform its stated function”. ... due to brand trust's ability for creating highly valued relationship (Chaudhuri & Holbrook, 2002). The brand trust is got by getting information of five-point scale like, this brand is worth trusting, this brand delivers the quality as promised, the confidence on this brand is always continuous and consistent, the brand has a good reputation and this is an honest brand.
Purchase Intention:
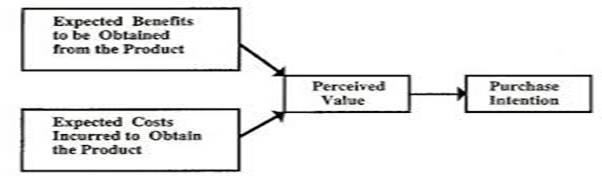
The willingness of a customer to buy a some product or a certain service is
known as purchase intention. Purchase intention is a dependent variable that depends on
several external and internal factors.
(source: www.google.co.in)
Purchase intention can be obtained from respondents thourgh questionnaire on five point scale. The information includes i) I would buy the product of this brand rather than any other brands available, ii) I intend to purchase the product of this brand in the future, iii) I actively encourage others to buy the product of this brand iv) I would like to buy the product of this brand for others as a gift and v) I wil not switch over the other brands even if an alternative brand offers more promotions on added value.
Objectives of the Study:
The following are the objectives of the study.
1. To study and analyse the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of televisions in Chennai.
2. To examine the impact of various demographic variables on purchase intention of consumers with regard to televisions in Chennai.
Stokes (1985) has given in his research that brand awareness can be the beginning step for the association of brand in mind and it denotes to the person’s ability to recall and remember the brand and its symbol or logo.
Buzzle and Gale (1987) They have studied the ROI and ROS has been impacted by perceived quality. Over the years of the product the most important factor which may have an impact on business can be the perceived quality.
Fornell (1992) analysed the following in their study that customer loyalty can be found by repeated purchase of the product even though the price of the brand tend to increase considerably.
Garbarino and Johnson (1999) proposed that the company has to constantly build and maintain brand trust because it is the fundamental characteristics for successful long run relationship between the company and the customer.
Jevons & Gabbott (2000) stated in their research paper that when the brand trusting relationships are created, the influence of brand association on trust will be the outcome expected of it.
Arthur Cheng ‐ Hsui Chen (2001) they have studied and identified the relation between brand association and brand equity and they concluded that there are two varieties of brand association that are product association and the other is organizational association.
Mowen and Minor (2001) they conclude in their research that customer decision follows a pattern beginning from identifying the problem, finding various solutions available, evaluating the various alternatives available for the problem and taking decisions.
Kotler (2003) has given that consumers attitudes and situations also can influence the purchase intention. The customer may change their preference if there is an unpredictable situation like price of the product being hiked, non-availability of brand of their choice etc.
Cathy J. Cobb-Walgren et al (2005) the study has given the consequences of brand equity. They have anlyzed the effect of brand equity on consumer preferences and purchase intentions.
Jamil Bojei et al (2012) they have studied the relationship between brand equity of smartphone and its relation to purchase intention. They have given the importance that brand equity is going to play in information technology.
Ashkan Yousefi (2016) has examined the effect of brand image on purchase intention in automative products. The data was analysed using spss tools and LISREL software. The conclusion was that brand image has positive effect on purchase intention.
Research Methodology:
The data for this case study has been collected from primary data and secondary data. Primary data was collected using a questionnaire and secondary data was collected from journals, articles etc. totally 650 data was collected and anlyzed using SPSS tools.
Table 1 -Demographic Profile
(Sample Size =650)
|
VARIABLES |
OPTIONS |
FREQUENCIES |
(%) |
|
Gender |
Male Female |
280 370 |
43.10 56.90 |
|
Age |
18 – 30 Years 31 - 50 Years 51 - 78 Years |
Open ended Question (Scale Variable) |
72.80 22.30 4.90 |
|
Qualification |
School Level Diploma UG / PG Professional |
121 101 311 117 |
18.60 15.50 47.80 18.00 |
|
Occupation |
Salaried Job Business / Self-employed Professional Student Home Maker |
253 112 115 36 134 |
38.90 17.20 17.70 5.50 20.60 |
|
Monthly Family Income (INR) |
Less than Rs.50,000 Rs.50,000 – Rs.1,00,000 Rs.1,00,001 – Rs.2,00,000 Above Rs.2,00,000 |
301 169 110 70 |
46.30 26.00 16.90 10.80 |
|
Marital Status |
Married Unmarried |
422 228 |
64.90 35.10 |
|
Type of Family |
Joint Family Nuclear Family |
222 428 |
34.20 65.80 |
Source: Primary Data
v The sample consists of a sizeable preponderance (280, 43.10%) of male respondents over female (370, 56.90%) respondents.
v 72.80% of the respondents belong to the age group of 18 - 30 years, followed by 22.30% of the respondents belong to the age group of 31 - 50 years and remaining 4.90% of the respondents belong to the age group of 51 - 78 years.
v In terms of academic qualifications, it is not surprising that majority (311, 47.80%) of the respondents completed UG/PG degrees followed by School level education with 18.60% (121).
v Majority of the respondents are Salaried employees (253, 38.90%) followed by Business/Self-employed with 17.20% (112), Professional (115, 17.70%), Students (36, 5.50%) and Home Maker (134, 20.60%).
v In terms of Monthly Family Income, majority of the respondents (301, 46.30%) belongs to the income of less than Rs.50,000 followed by Rs.50,000 – Rs.1,00,000 (169, 26%), Rs.1,00,001 – Rs.2,00,000 (110, 16.90%) and Above Rs.2,00,000 (70, 10.80%).
v Majority of the respondents are Married (422, 64.90%) and remaining (228, 35.10%) of the respondents are Unmarried.
v In terms of type of family, 65.80% (428) of the respondents are from Nuclear family and rest of them (222, 34.20%) belong to Joint Family.
Table 2 -TELEVISION (Entertainment Product)
(Sample Size =650)
|
VARIABLES |
OPTIONS |
FREQUENCIES |
(%) |
|
Name of the Brand |
Samsung LG Sony Videocon Others |
285 221 101 17 26 |
43.80 34.00 15.50 2.60 4.00 |
|
Years of Usage |
1 – 3 Years 4 – 6 Years 7 – 11 Years |
Open ended Question (Scale Variable) |
15.80 49.00 35.20 |
Source: Primary Data
v Majority of the respondents used the Television (Home Appliance), Samsung (285, 43.80%) followed by LG with 34% (221), Sony (101, 15.50%), Videocon (2.60%, 17) and other brands (26, 4%).
v In terms of Years of Usage of Television, 15.80% of the respondents used 1 – 3 Years, 49% of them used 4 – 6 Years and 35.20% of them used 7 – 11 Years.
Table 3- BRAND TRUST (BT)
|
Descriptive Statistics |
|||
|
|
N |
Mean |
SD |
|
This brand is worth trusting |
650 |
3.95 |
.501 |
|
This brand delivers the quality as promised |
650 |
3.82 |
.666 |
|
The confidence on this brand is always continuous and consistent |
650 |
3.58 |
.793 |
|
This brand has a good reputation |
650 |
3.75 |
.625 |
|
This is an honest brand |
650 |
3.72 |
.452 |
|
BRAND TRUST (BT) |
650 |
18.81 |
2.309 |
Source: Primary Data
v From the above table, it is found that the mean score(M=3.95) of the variable - “ This brand is worth trusting” is more than other variables.
v It is also found that the respondents have more Brand Trust (BT) with respect to the television since the mean score of all the variables are above 3.5 (70%) out of 5.
Table 4 -IMPACT OF BRAND TRUST ON PURCHASE INTENTION
Descriptive Statistics
|
N |
Mean |
SD |
|
|
I would buy the product of this brand rather than any other brands available |
650 |
3.28 |
.895 |
|
I intend to purchase the product of this brand in the future |
650 |
3.43 |
.702 |
|
I actively encourage others to buy the product of this brand |
650 |
3.75 |
.807 |
|
I would like to buy the product of this brand for others as a gift |
650 |
3.57 |
.823 |
|
I will not switch over to other brands even if an alternative brand offers more promotions or added values |
650 |
3.12 |
1.039 |
|
IMPACT OF BRAND TRUST ON PURCHASE INTENTION |
450 |
17.69 |
3.518 |
Source: Primary Data
v From the above table, it is found that the mean score (M = 3.75) of the variable – “ I actively encourage others to buy the product of this brand ” is more than other variables.
v It is also found that the mean score of all the variables relating to “Impact of Brand trust on Purchase Intention towards the television” are above 3 (60%) out of 5. This indicates that the impact of brand trust on purchase intention towards television is considerably more.
H 0 -HYPOTHESIS 1
H0: There is no significant difference between the Male and Female respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of Television.
TABLE 5 - Gender
|
VARIABLES |
GENDER |
t - value |
p - value |
|||||
|
MALE |
FEMALE |
|||||||
|
N |
Mean |
SD |
N |
Mean |
SD |
|||
|
I would buy the product of this brand rather than any other brands available |
280 |
3.42 |
1.217 |
370 |
2.98 |
1.200 |
3.689 |
0.000 |
|
I intend to purchase the product of this brand in the future |
280 |
3.89 |
0.943 |
370 |
3.65 |
1.010 |
2.461 |
0.014 |
|
I actively encourage others to buy the product of this brand |
280 |
3.62 |
1.004 |
370 |
3.41 |
1.259 |
1.743 |
0.043 |
|
I would like to buy the product of this brand for others as a gift |
280 |
4.05 |
0.927 |
370 |
3.57 |
1.146 |
4.499 |
0.000 |
|
I will not switch over to other brands even if an alternative brand offers more promotions or added values |
280 |
3.70 |
1.169 |
370 |
3.86 |
1.176 |
1.419 |
0.157 |
|
IMPACT ON PURCHASE INTENTION |
280 |
18.68 |
3.425 |
370 |
17.47 |
4.005 |
3.175 |
0.002 |
v Source: Primary Data
An independent-samples t-test was conducted to compare the difference between Male and Female respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television.
v
|
VARIABLES |
t - Value |
P - Value |
Level of significance |
RESULT |
|
|
Significance |
Null Hypothesis |
||||
|
I would buy the product of this brand rather than any other brands available |
3.689 |
0.000 |
0.01 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
I intend to purchase the product of this brand in the future |
2.461 |
0.014 |
0.05 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
I actively encourage others to buy the product of this brand |
1.743 |
0.043 |
0.05 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
I would like to buy the product of this brand for others as a gift |
4.499 |
0.000 |
0.01 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
I will not switch over to other brands even if an alternative brand offers more promotions or added values |
1.419 |
0.157 |
0.05 |
Insignificant |
ACCEPTED |
|
IMPACT ON PURCHASE INTENTION |
3.175 |
0.002 |
0.01 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
v As the P value is lesser than Sig. Value (0.05 and 0.01) in 5 variables, including Impact on purchase intention Score, the Null Hypotheses are rejected. The Null hypothesis is accepted in only one aspect, since the P (0.157) value is greater than Sig. Value (0.05). Hence, it is concluded that there is a statistically significant difference between Male and Female respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television.
v Based on the mean scores of Impact on Purchase Intention, we can say that the mean value of the above variable is little more for male respondents (M=18.68) than the female respondents (M=17.47). It indicates that the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television is more for male respondents than the female respondents.
v Overall, there is a significant difference between the Male and Female respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television.
H0: HYPOTHESIS 2
H0: There is no significant difference between the Married and Unmarried respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television.
v
TABLE 5 – Marital Status
|
VARIABLES |
MARITAL STATUS |
t - value |
p - value |
|||||
|
MARRIED |
UNMARRIED |
|||||||
|
N |
Mean |
SD |
N |
Mean |
SD |
|||
|
I would buy the product of this brand rather than any other brands available |
422 |
3.75 |
0.533 |
228 |
4.44 |
0.498 |
4.859 |
0.001 |
|
I intend to purchase the product of this brand in the future |
422 |
3.97 |
0.627 |
228 |
4.14 |
0.347 |
4.417 |
0.001 |
|
I actively encourage others to buy the product of this brand |
422 |
3.67 |
0.710 |
228 |
2.88 |
1.442 |
6.485 |
0.001 |
|
I would like to buy the product of this brand for others as a gift |
422 |
3.63 |
0.861 |
228 |
2.88 |
1.442 |
6.095 |
0.001 |
|
I will not switch over to other brands even if an alternative brand offers more promotions or added values |
422 |
3.64 |
0.987 |
228 |
3.66 |
0.711 |
0.269 |
0.788 |
|
IMPACT ON PURCHASE INTENTION |
422 |
18.65 |
2.624 |
228 |
18.00 |
3.906 |
1.941 |
0.044 |
v Source: Primary Data
v An independent-samples t-test was conducted to compare the difference between the Married and Unmarried respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television.
v
|
VARIABLES |
t - Value |
P - Value |
Level of significance |
RESULT |
|
|
Significance |
Null Hypothesis |
||||
|
I would buy the product of this brand rather than any other brands available |
4.859 |
0.001 |
0.01 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
I intend to purchase the product of this brand in the future |
4.417 |
0.001 |
0.01 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
I actively encourage others to buy the product of this brand |
6.485 |
0.001 |
0.01 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
I would like to buy the product of this brand for others as a gift |
6.095 |
0.001 |
0.01 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
I will not switch over to other brands even if an alternative brand offers more promotions or added values |
0.269 |
0.788 |
0.05 |
Insignificant |
ACCEPTED |
|
IMPACT ON PURCHASE INTENTION |
1.941 |
0.044 |
0.05 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
v As the P value is lesser than Sig. Value (0.05 and 0.01) in 5 variables including Impact on purchase intention Score, the Null hypotheses are rejected. The Null Hypothesis is accepted in only one aspect, since the P (0.788) value is greater than Sig. Value (0.05). Hence, it is concluded that there is a statistically significant difference between the Married and Unmarried respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television.
v Based on the mean scores of Impact on Purchase Intention, we can say that the mean score of the above variable is little more for married respondents (M=18.65) than the unmarried respondents (M=18.00). It indicates that the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television is more for married respondents than the unmarried respondents.
v Overall, there is a significant difference between the Married and Unmarried respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television.
v
H0: HYPOTHESIS 3
H0: There is no significant difference between the Joint Family and Nuclear Family with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television.
v
v
TABLE 6 – Type of Family
|
VARIABLES |
TYPE OF FAMILY |
t - value |
p - value |
|||||
|
JOINT FAMILY |
NUCLEAR FAMILY |
|||||||
|
N |
Mean |
SD |
N |
Mean |
SD |
|||
|
I would buy the product of this brand rather than any other brands available |
222 |
3.64 |
0.612 |
428 |
3.25 |
0.432 |
8.927 |
0.001 |
|
I intend to purchase the product of this brand in the future |
222 |
3.77 |
0.868 |
428 |
3.56 |
0.498 |
3.781 |
0.001 |
|
I actively encourage others to buy the product of this brand |
222 |
3.63 |
0.972 |
428 |
3.14 |
0.347 |
9.823 |
0.001 |
|
I would like to buy the product of this brand for others as a gift |
222 |
3.65 |
0.681 |
428 |
3.00 |
0.000 |
6.494 |
0.001 |
|
I will not switch over to other brands even if an alternative brand offers more promotions or added values |
222 |
3.81 |
0.874 |
428 |
3.84 |
0.644 |
0.502 |
0.616 |
|
IMPACT ON PURCHASE INTENTION (PI) |
222 |
18.50 |
3.144 |
428 |
16.79 |
1.495 |
9.457 |
0.001 |
v Source: Primary Data
An independent-samples t-test was conducted to compare the difference between the Joint family respondents and Nuclear family respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television.
|
VARIABLES |
t - Value |
P - Value |
Level of significance |
RESULT |
|
|
Significance |
Null Hypothesis |
||||
|
I would buy the product of this brand rather than any other brands available |
8.927 |
0.001 |
0.01 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
I intend to purchase the product of this brand in the future |
3.781 |
0.001 |
0.01 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
I actively encourage others to buy the product of this brand |
9.823 |
0.001 |
0.01 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
I would like to buy the product of this brand for others as a gift |
6.494 |
0.001 |
0.01 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
I will not switch over to other brands even if an alternative brand offers more promotions or added values |
0.502 |
0.616 |
0.05 |
Insignificant |
ACCEPTED |
|
IMPACT ON PURCHASE INTENTION (PI) |
9.457 |
0.001 |
0.01 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
v As the P value is lesser than Sig. Value (0.01) in 5 variables including Impact on Purchase Intention Score, the Null Hypotheses are rejected. The Null hypothesis is accepted in only one case, since the P (0.616) value is greater than Sig. Value (0.05). Hence, it is concluded that there is a statistically significant difference between the Joint family and Nuclear family respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television.
v Based on the mean scores of Impact on Purchase Intention, we can say that the mean score of the above variable is more for Joint family respondents (M=18.50) than the Nuclear family respondents (M=16.79). It indicates that the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television is more for Joint family than the Nuclear family respondents.
v Overall, there is a significant difference between the Joint family respondents and Nuclear family respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television.
HYPOTHESIS 4
H0: There is no significant difference among the Qualification of the respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television .
v
TABLE 7 - Qualification
|
VARIABLE |
QUALIFICATION |
F - value |
p - value |
|||
|
School Level (121) |
Diploma (101) |
UG / PG (311) |
Professional (117) |
|||
|
I would buy the product of this brand rather than any other brands available |
3.79 |
4.13 |
3.86 |
3.74 |
1.972 |
0.043 |
|
1.116 |
0.875 |
0.962 |
1.152 |
|||
|
I intend to purchase the product of this brand in the future |
3.91 |
3.96 |
3.81 |
3.91 |
1.964 |
0.033 |
|
0.885 |
0.990 |
1.016 |
1.086 |
|||
|
I actively encourage others to buy the product of this brand |
4.05 |
4.25 |
4.04 |
3.50 |
5.332 |
0.000 |
|
0.932 |
0.837 |
0.892 |
1.129 |
|||
|
I would like to buy the product of this brand for others as a gift |
4.03 |
4.23 |
3.98 |
4.02 |
2.288 |
0.035 |
|
1.003 |
1.027 |
1.037 |
1.055 |
|||
|
will not switch over to other brands even if an alternative brand offers more promotions or added values |
4.05 |
4.16 |
4.01 |
3.80 |
1.970 |
0.040 |
|
0.977 |
0.949 |
0.948 |
0.959 |
|||
|
PURCHASE INTENTION |
19.84 |
20.73 |
19.71 |
18.96 |
3.878 |
0.018 |
|
3.843 |
3.816 |
3.972 |
4.198 |
|||
v Source: Primary Data No. of respondents are shown in brackets
v
v
v A one-way between-groups analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted to explore the significant difference among the Qualification of the respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television.
v
v
v
|
VARIABLE |
F - Value |
P - Value |
Level of significance |
RESULT |
|
|
Significance |
Null Hypothesis |
||||
|
I would buy the product of this brand rather than any other brands available |
1.972 |
0.043 |
0.05 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
I intend to purchase the product of this brand in the future |
1.964 |
0.033 |
0.05 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
I actively encourage others to buy the product of this brand |
5.332 |
0.000 |
0.01 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
I would like to buy the product of this brand for others as a gift |
2.288 |
0.035 |
0.05 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
will not switch over to other brands even if an alternative brand offers more promotions or added values |
1.970 |
0.040 |
0.05 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
PURCHASE INTENTION |
3.878 |
0.018 |
0.05 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
As the P value is lesser than Sig. Value (0.01 and 0.05), the Null Hypothesis is rejected. Hence, it is concluded that there is a statistically significant difference among the Qualification of the respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television.
v Apart from reaching statistical significance, the actual difference in mean scores among the Qualification of the respondents is also moderate (18.84 to 20.73).
v Thus, there is no significant difference among the Qualification of the respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of televisions .
HYPOTHESIS 5
H0: There is no significant difference among the Occupation of the respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television .
v TABLE 8 – Occupation
|
VARIABLE |
OCCUPATION |
F - value |
p - value |
||||
|
Salaried Job (253) |
Business / Self-employed (112) |
Professional (115) |
Student (36) |
Home Maker (134) |
|||
|
I would buy the product of this brand rather than any other brands available |
3.99 |
3.78 |
3.88 |
3.67 |
3.99 |
4.100 |
0.003 |
|
0.913 |
1.086 |
0.946 |
1.074 |
0.913 |
|||
|
I intend to purchase the product of this brand in the future |
3.75 |
4.09 |
3.93 |
4.15 |
3.75 |
3.259 |
0.012 |
|
0.979 |
0.976 |
1.050 |
0.949 |
0.979 |
|||
|
I actively encourage others to buy the product of this brand |
4.08 |
4.04 |
3.60 |
4.11 |
4.08 |
3.345 |
0.010 |
|
0.820 |
1.108 |
0.923 |
0.974 |
0.820 |
|||
|
I would like to buy the product of this brand for others as a gift |
3.97 |
4.15 |
4.07 |
3.93 |
3.97 |
1.582 |
0.178 |
|
1.006 |
0.992 |
0.942 |
1.174 |
1.006 |
|||
|
will not switch over to other brands even if an alternative brand offers more promotions or added values |
4.09 |
4.01 |
3.70 |
4.07 |
4.09 |
2.035 |
0.028 |
|
0.899 |
1.023 |
0.981 |
0.829 |
0.899 |
|||
|
PURCHASE INTENTION |
21.89 |
20.07 |
19.18 |
19.93 |
18.89 |
1.993 |
0.039 |
|
3.572 |
4.393 |
3.869 |
4.113 |
3.572 |
|||
v Source: Primary Data No. of respondents are shown in brackets
v A one-way between-groups analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted to explore the significant difference among the Occupation of the respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television.
|
VARIABLE |
F - Value |
P - Value |
Level of significance |
RESULT |
|
|
Significance |
Null Hypothesis |
||||
|
I would buy the product of this brand rather than any other brands available |
4.100 |
0.003 |
0.05 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
I intend to purchase the product of this brand in the future |
3.259 |
0.012 |
0.05 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
I actively encourage others to buy the product of this brand |
3.345 |
0.010 |
0.05 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
I would like to buy the product of this brand for others as a gift |
1.582 |
0.178 |
0.05 |
Insignificant |
ACCEPTED |
|
will not switch over to other brands even if an alternative brand offers more promotions or added values |
2.035 |
0.028 |
0.05 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
PURCHASE INTENTION |
1.993 |
0.039 |
0.05 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
v As the P value is lesser than Sig. Value (0.05) in 5 variables including Purchase Intention Score, the Null hypotheses is rejected. The Null hypotheses is accepted in only one case, since the P value is greater than Sig. Value (0.05) the Null Hypothesis is accepted. Hence, it is concluded that there is a statistically significant difference among the Occupation of the respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television.
v Apart from reaching statistical significance, the actual difference in mean scores among the Occupation of the respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television is also moderate (18.89 to 21.89)
v Hence, there is a significant difference among the Occupation of the respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television.
HYPOTHESIS 6
H0: There is no significant difference among the Income levels of the respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television .
v TABLE 9 - Income
|
VARIABLE |
INCOME |
F - value |
p - value |
|||
|
Less Than Rs.50,000 (301) |
Rs.50,000 – Rs.1,00,000 (169) |
Rs.1,00,001 – Rs.2,00,000 (110) |
Above Rs.2,00,000 (70) |
|||
|
I would buy the product of this brand rather than any other brands available |
3.80 |
3.98 |
3.81 |
3.84 |
1.089 |
0.353 |
|
0.982 |
1.143 |
0.868 |
0.805 |
|||
|
I intend to purchase the product of this brand in the future |
3.85 |
4.13 |
3.74 |
3.93 |
5.211 |
0.002 |
|
1.008 |
0.949 |
0.909 |
0.974 |
|||
|
I actively encourage others to buy the product of this brand |
3.92 |
4.21 |
4.07 |
4.27 |
7.151 |
0.000 |
|
1.009 |
0.917 |
0.672 |
0.624 |
|||
|
I would like to buy the product of this brand for others as a gift |
3.89 |
4.18 |
4.26 |
3.73 |
4.865 |
0.002 |
|
1.043 |
1.161 |
0.690 |
0.788 |
|||
|
I will not switch over to other brands even if an alternative brand offers more promotions or added values |
3.98 |
4.17 |
3.86 |
4.20 |
3.185 |
0.024 |
|
1.002 |
0.890 |
0.999 |
0.701 |
|||
|
PURCHASE INTENTION |
18.90 |
20.67 |
19.74 |
19.98 |
4.703 |
0.003 |
|
4.210 |
3.791 |
3.104 |
3.008 |
|||
Source: Primary Data No. of respondents are shown in brackets
v A one-way between-groups analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted to explore the significant difference among the Income levels of the respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television.
v
v
v
|
VARIABLE |
F - Value |
P - Value |
Level of significance |
RESULT |
|
|
Significance |
Null Hypothesis |
||||
|
I would buy the product of this brand rather than any other brands available |
1.089 |
0.353 |
0.05 |
Insignificant |
ACCEPTED |
|
I intend to purchase the product of this brand in the future |
5.211 |
0.002 |
0.05 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
I actively encourage others to buy the product of this brand |
7.151 |
0.000 |
0.01 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
I would like to buy the product of this brand for others as a gift |
4.865 |
0.002 |
0.05 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
will not switch over to other brands even if an alternative brand offers more promotions or added values |
3.185 |
0.024 |
0.05 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
|
PURCHASE INTENTION |
4.703 |
0.003 |
0.05 |
Significant |
REJECTED |
v As the P value is lesser than Sig. Value (0.01 and 0.05) in 5 cases, including Purchase Intention Score, the Null Hypotheses are rejected. The Null Hypothesis is accepted in only one case, since the P (0.353) value is greater than Sig. Value (0.05). Hence, it is concluded that there is a statistically significant difference among the Income levels of the respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television.
v Apart from reaching statistical significance, the actual difference in mean scores among the Income of the respondents is also moderate (18.90 to 20.67).
v Thus, there is a significant difference among the Income levels of the respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television.
1. The sample consists of a sizeable preponderance (280, 43.10%) of male respondents over female (370, 56.90%) respondents. 72.80% of the respondents belong to the age group of 18 - 30 years, followed by 22.30% of the respondents belong to the age group of 31 - 50 years and remaining 4.90% of the respondents belong to the age group of 51 - 78 years. In terms of academic qualifications, it is not surprising that majority (311, 47.80%) of the respondents completed UG/PG degrees followed by School level education with 18.60% (121).Majority of the respondents are Salaried employees (253, 38.90%) followed by Business/Self-employed with 17.20% (112), Professional (115, 17.70%), Students (36, 5.50%) and Home Maker (134, 20.60%).In terms of Monthly Family Income, majority of the respondents (301, 46.30%) belongs to the income of less than Rs.50,000 followed by Rs.50,000 – Rs.1,00,000 (169, 26%), Rs.1,00,001 – Rs.2,00,000 (110, 16.90%) and Above Rs.2,00,000 (70, 10.80%).Majority of the respondents are Married (422, 64.90%) and remaining (228, 35.10%) of the respondents are Unmarried.
2. Majority of the respondents used the Television (Home Appliance), Samsung (285, 43.80%) followed by LG with 34% (221), Sony (101, 15.50%), Videocon (2.60%, 17) and other brands (26, 4%). In terms of Years of Usage of Television, 15.80% of the respondents used 1 – 3 Years, 49% of them used 4 – 6 Years and 35.20% of them used 7 – 11 Years.
3. It is found that the mean score (M=3.95) of the variable - “This brand is worth trusting” is more than other variables. It is also found that the respondents have more Brand Trust (BT) with respect to the television since the mean score of all the variables are above 3.5 (70%) out of 5.
4. It is found that the mean score (M = 3.75) of the variable – “ I actively encourage others to buy the product of this brand” is more than other variables. It is also found that the mean score of all the variables relating to “Impact of Brand trust on Purchase Intention towards the television” are above 3 (60%) out of 5. This indicates that the impact of brand trust on purchase intention towards television is considerably more.
5. As the P value is lesser than Sig. Value (0.05 and 0.01) in 5 variables, including Impact on purchase intention Score, the Null Hypotheses are rejected. The Null hypothesis is accepted in only one aspect, since the P (0.157) value is greater than Sig. Value (0.05). Hence, it is concluded that there is a statistically significant difference between Male and Female respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television. Based on the mean scores of Impact on Purchase Intention, we can say that the mean value of the above variable is little more for male respondents (M=18.68) than the female respondents (M=17.47). It indicates that the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television is more for male respondents than the female respondents. Overall, there is a significant difference between the Male and Female respondents with respect to the impact of brand trust on purchase intention of television.
From the above analysis it is clear that brand trust has a strong impact on the purchase intention of television. Competition and innoviation are not new to this filed i.e television industry. If the marketer tries to understand these concepts they will be able to sell better and profitably.
Suggestions:
1. Marketers can think of ways to improve brand trust so that the purchase intention for the particular brand will be higher.
2. After sales service is one of the important thing the customer is concerned about. Marketers if they give good after sales service the brand trust can be improved.
3. Regular advertisement will also make the customer remember the brand,
4. Any product improvement or product renovation must be intimated to existing customer so that they prefer to buy the particular brand they trust.
1. Fishbein, M., &Ajzen, I. (1975). Belief, attitude, intention and behavior: An introduction to theory and research. Reading, Mass: Addison-Wesley.
2. Engel, J. F. Blackwell, R. D., &Miniard, P. W. (1995). Consumer behavior (8th Ed.) New York: Dryden Press. Farr A., & Hollis, N. (1997). What do you want your brand to be when it grows up? Big and strong? Journal of Advertising Research, 37(6), 23-36.
3. Stokes RC (1985). The Effects of Price, Package Design, and Brand Familiarity on Perceived quality.
4. Kotler, P. (2003). Strategic Marketing for Non-profit Organizations (6th Eds.). Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Pearson /Prentice-Hall.
5. Buzzle, R. D., & Gale, B. T. (1987). The PIMS principles: Linking strategy to performance. Free Press, New York.
6. Fornell, C. (1992). A National Customer Satisfaction Barometer: The Swedish Experience. Journal of Marketing Research, 56(January), 6-21.
7. Johnson, and Seymour Sudman (1999), “Understanding Consumer Usage of Product Magnitudes through Sorting Tasks,” Psychology & Marketing 16 (8), 643-57.
8. HsinKuang Chi and Dr.Huery Ren Yeh (2009) The Impact of Brand Awareness on Consumer Purchase Intention: The Mediating Effect of Perceived Quality and Brand Loyalty The Journal of International Management Studies, Volume 4, Number 1, February, 2009 PP(135-144).
9. Mowen, J. C., & Minor, M. (2001). Consumer behavior: A framework (2nd Ed.). Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice-Hall.
10. Jamil Bojei& Wong Chee Hoo : International Journal of Business and Society, Vol. 13 No. 1, 2012, 33 – 48.
Cathy J. Cobb-Walgren& Cynthia A. Ruble and Naveen Donthu, journal of advertising, volume XXIV, Number 3, Fall 1995.
11. R. Patel Niraj 2009, “Consumer attitude towards Air Conditioners of Blue Star in Surat City, Maniba Institute of Business management. Page no.36-55