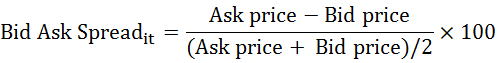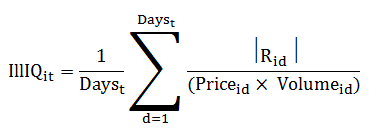A Refereed Monthly International Journal of Management
The Impact of Information Asymmetry and Liquidity Risk on Financial Flexibility:
A case study of selected Corporations of Tehran Stock Exchange
Author
|
Hanieh Karimi
Department of Accounting
Kermanshah Branch
Islamic Azad University
Kermanshah, Iran
|
Babak Jamshidinavid
Department of Accounting
Kermanshah Branch
Islamic Azad University
Kermanshah, Iran
E-mail:- jamshidinavid@iauksh.ac.ir
|
Abstract
The present study is examining the impact of information asymmetry and liquidity
risk on financial flexibility of the selected corporations listed in Tehran Stock
Exchange. The present research is applied in term of its endeavor and also sectional
as it is based on time. The quantitative data is used and the research design is
descriptive and causal as it is examining the relationship between variables such
as information asymmetry, liquidity risk and financial adaptability. For the study
148 listed corporations of Tehran Stock Exchange has been selected for the study
and have been studied between year 2012 to year 2016. In the research, information
asymmetry and liquidity risk of stock are independent variables and their effects
on financial flexibility as the dependent variable in the form of regression model
based on paneling data have been experimentally tested. The research conclusions
indicate that information asymmetry has negative yet significant impact on financial
flexibility while liquidity risk of stock has significant positive consequence on
financial flexibility. All together effect of information asymmetry and liquidity
risk variables on financial flexibility is negative and yet significant. Eventually,
on the basis of conclusions inferred from tests of hypotheses, it can be suggested
that managers should perform suitable functions such as; appropriate disclosure,
accuracy of financial structure, supplement of suitable financial support and reducing
unsuitable conservation. With the help of above mentioned actions, domain difference
of sale and buy bid price and risk of stock liquidity will decrease which will lead
to more financial flexibility. Moreover, it is suggested that investors should look
into extent of risk liquidity of stock in while making investment and they should
avoid investment when the difference of sale and buy price is higher than the corporation
buying stock.
Keywords : Information Asymmetry, Liquidity Risk of Stock, Financial
Flexibility.
Introduction
One of the most imperative factors in investment decision making is suitable and
relative information. If required information’s are distributed asymmetrically (information
transformation will be done unequally between individuals), it can lead to different
conclusions about the subject. It is more important to evaluate Quality information
available rather than information available to the investment decision maker. While
information asymmetry increases of a corporation, its potential value will be different
from a value that investors distinguish in capital market for intended stock. Finally,
stock real values of corporations will be different from expected values by investors.
What is considered in capital markets is that the most of the individuals who invest
in the stock market are normal people and their only ways to access important information,
are the information which are published by corporations. One of these kinds of publications
is annual financial reports where announcement of each share profit and profit is
anticipated by corporations and then is announced for public. If there are individuals
who have more information among investors, who are active in capital markets, will
be in better situations than others because they are aware of announcements about
profit so, they can influence on market supply and demand. Otherwise, they can cause
price spread. The main reason is existence of information asymmetry in capital market
and based on it informative individuals of profit announcement (or important news)
will be situated in better conditions than others. One of the important points that
should always be suggested in capital market especially in Tehran Stock Exchange
id efficiency discussion and based on it existent information in market will reflex
their effects on price stock. The reason for existence of accounting can be defined
as information asymmetry that one of the transaction part has more formation than
another part based on efficiency market hypothesis. This factor is because of internal
transaction and information, (Ghaemi & Vatanparast, 2004).
Investment refinement in a stock depends on liquidity power of its stock which is
one of the dimensions of optimized division process. In fact, liquidity risk is
the main characteristics market sub structural factors that risks individual capital
and play very important roles in investors decisions for buy and sale of their stocks.
Eventually it can be said that liquidity is one of the big sources of risk for investors,
(Piqueria, 2006). Lack of liquidity occurs when stock price in reactions to few
shocks changes rapidly. In fact, lack of liquidity may have negative effect on stock
value, (Martinez & Miguel, 2005). Liquidity is a simple recusant concept that
will not be directly visible. Liquidity easiness and change of an asset to cash
flow is called liquidity, (Pastor & Stambaugh, 2003).
One of the characteristics of commercial units that can help managers to maximize
corporation value is maintaining financial flexibility. Financial flexibility is
organizational ability in recognition of changes, opportunities and threats, rapid
and effective adaptation with new situations to receive suitable performance. Flexibility
can play important role in empowering mangers about use of investment opportunities
in future and capital market problems has made keeping financial flexibility for
corporations to use profitable opportunities. Myers, (1984), indicated that ow threats
of corporations` liabilities can stop their uses of profitable opportunities and
evaluating of commercial unit even when managers and shareholders are interested
in using opportunities, (Khodaeivalehzaghrad & Raretaimori, 2009). Optimized
reservation of sources can cause corporations to be successful in market and corporations
can follow market opportunities successfully and they should benefit from activity
benefits in market. Based on the mentioned factors, this research is investigating
the effect of information asymmetry and liquidity risk of stock on financial flexibility
of corporations.
Research Background
Khadarahmi & et.al. (2015), in their research on “The effect of information
asymmetry on stock price future downfall risk of the accepted corporations in Tehran
Stock Exchange”, concluded that in the situation of lack of information asymmetry,
stock price will fall and lead to increased risk because of non-existence of current
flow of information between managers and investors.
Shaerianaghiz & et.al. (2015), in their research “Relationship between financial
flexibility and kind of financial supplement of the accepted corporations in Tehran
Stock Exchange”, concluded that financial flexibility had positive yet significant
relationship.
Habibisaamr & et.al. (2014), in their research “Relationship between liquidity
risk and market risk with growing stock return and AHP valuing in Tehran Stock Exchange”,
concluded that there was a linear inverse relationship between risk and stock’s
real return.
Bonaime & et.al. (2016), in their research “Financial flexibility expense: observations
of stock rebuy” pointed out that correlation between financial flexibility and corporations
management was less than that of correlation between financial flexibility and profit.
Increase of profit management amount would increase financial flexibility expense
while increase of amount of institutional management supervision would decrease
financial flexibility expense.
De La Bruslerie & Latrous (2014), found that there was a positive meaningful
relationship between ownership structure and leverage indicators of financial flexibility.
Theoretical Bases
Conceptual Definitions
Information Asymmetry
If one part of transaction in a transaction has more information than other part,
there will be information asymmetry, (Ghaemi & Vatanparast, 2004).
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk occurs when an individual investor, business or financial institution
cannot meet short-term debt obligations. The investor or entity may be unable to
convert an asset into cash without giving up capital and/or income due to a lack
of buyers or an inefficient market. If owner of stock exchange can`t sell his stock
easily in one secondary market, this factor will cause a kind of risk for him. While
liquidity is higher in stock exchange market, amount of this risk will decrease.
While process change of an asset to cash flow is long or possibility of this change
encounters with doubts, it will have liquidity risk, (Chan & et.al. 2007).
Financial Flexibility
Financial flexibility is the corporation ability to encounter unexpected pauses
in cash flow. It means that ability of demanding loan from different sources, capital
increase, and sale of properties and guidance of corporation operations are for
facing with variable situations. Moreover, financial flexibility based on accounting
standard is ability of commercial unit in term of effective performances to change
amount and time of its cash flows in such a way to show necessary reflection about
unexpected events, (Bagherbaigi, 2011).
Corporation Size
Corporation size means activity mass and amount of a corporation. Corporation size
is an important factor that may effect on capital and accessible amount to cash
flow by different sources.
Growth Opportunities
It is market value ratio to clerical value of shareowners` rights and it is a measurement
criterion for corporation growth.
Operational Definitions
Information Asymmetry
To calculate information symmetry in Tehran Stock Exchange following model will
be used. This model has been used for the first time by Venkatesh & Chiang in
1986 to determine bid price domain to buy and sell stock. Then, other individuals
have used this model in their researchers; the mentioned model is as follow:
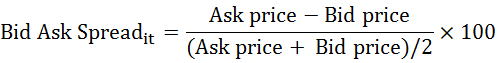
Bid Ask Spread it: domain of suggesting price for buy and sale of i corporation
stock in t duration.
Ask Price: average of suggesting price for sale of i corporation stock in t duration.
Bid Price: average of suggesting price for buying of i corporation stock in t duration.
Liquidity Risk
Criterion of liquidity risk is Amicus in this research that is expressed as follow;
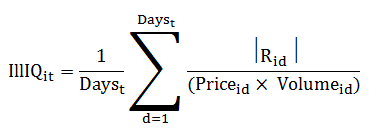
IIIQ it= ratio of lack of i stock liquidity in t duration
R id= yearly absolute return of i stock in d day
Price id= i stock price in d day
Volume id= numbers of i stocks in d day in transaction market
Days t= numbers of days that in t duration the possibility of i stock
transaction performance in market will be.
While daily average of transaction mass is high, stock will have high liquidity
and can be transacted easily in market. If daily average of transaction mass is
high, its market price will have lesser changeability because transactions should
be big enough to have effect on stock market price. The above formula numerator
indicates stock daily absolute return that has positive relationship with change
of stock market price. While price constancy is more in market, the formula numerator
will be smaller. Finally, it can be said that higher amount of Amihud lack of liquidity
standard has relationship with lower liquidity of market, (vice versa).
Financial Flexibility
Financial leverage= clerical value of total liability / clerical value of total
properties
Growth Opportunities
In this research, growth opportunity is used as controlling variable that is calculated
as:
Growth opportunity= market value / clerical value
Corporation size
In this research, corporation size is used as controlling variable that is calculated
as:
Corporation size= Ln (yearly pure sale mass)
Research Methodology
Every research should have special research design and method should be used on
the basis of relevant objectives, should use suitable method and instrument to gather
and analyze data that. The research is “applied” in term of its objectives, and
it is “sectional” based on its time. The data used in the research is “quantitative”
whereas the research performance method is “descriptive.. All Statistic population
includes 856 corporations and 148 corporations have been chosen as the research
statistic sample by systematic deletion. In this research, at first random method
was used to gather data and information. In the library part, research theoretical
bases have been gathered from Persian and Latin special books and magazines, and
then the research data have been done by data gathering of chosen corporations by
reference tom their financial statements, descriptive footnotes, weekly reports
and monthly stock exchange through Rahavard Novin Software. Finally, tests of hypotheses
will be done by accumulation of gathered data and doing considerable calculations.
Research Hypotheses
First Hypothesis: Information asymmetry has significant effect on financial flexibility
of corporations.
Second Hypothesis: liquidity risk has significant effect on financial flexibility
of corporations.
Third Hypothesis: information asymmetry and liquidity risk have significant effects
on financial flexibility of corporations.
Specification of Test Kind and Method of Analysis
The statistical tests have been used to check data and to recognize homogeneity
or in homogeneity of research data. Chow Test and F Limer Statistic have been used.
Statistic hypotheses of this test will be described as follow:
H0: Pooling Data
H1: Panel Data
While this test conclusions are based on paneling data use, fixed effects or random
effects models should be used to estimate research model. Husman Test should be
performed to choose one the models.
H0: Random Effects
H1: Fixed Effects
Table 1: conclusions of Chow Test to recognize homogeneity or in homogeneity of
sections
|
Hypothesis test
|
F
|
Statistical probability of F
|
Result of Chow Test
|
|
Research model
|
14.501
|
0.000
|
Paneling data
|
As indicated in the above table, Chow Test conclusion represents that received probability
for F statistic in all research hypotheses is less than 5 percent, so this hypothesis
test data in all models will be use as paneling.
Hausman Test
In this test, Chi-square statistic with K freedom degree will be used. If received
Chi-Du is more than table amount, null hypothesis of random effects will be rejected
and fixed effects hypothesis will be accepted.
Table2: conclusions of Hausman Test to recognize use of fixed or random effects
|
Hypothesis test
|
Statistic amount
|
Statistical probability
|
Test result
|
|
Research model
|
49.030
|
0.000
|
Fixed effects
|
In this test H0 is based on data paneling model with random effects and its contrast
hypothesis, H1 is based on data paneling model with fixed effects. If statistic
of Hausman test is bigger than its crisis amounts or its probability is less than
5 percent, H0 will be rejected and use of fixed effects model will be accepted.
Based on received conclusions of Hausman Test for the research model, while error
is 5 percent, amount of Hausman statistic for this model will be 49.030 and P-Value
<0.05, so H0 will be rejected. Rejection of H0 indicates that method of random
effects is not homogenous and fixed effects method should be used.
Test Conclusions of the Research Hypotheses
In this study, model estimation method is based on panel data. This method is based
on time series information from 2012 to 2016 of 148 accepted corporations` data
in Tehran Stock Exchange. All the estimated numbers for each model variables will
be based on Million Rial. Used software program in this research is Eviews 8 software.
Estimated models have been introduced based ob exhibited hypotheses as regression
models of multi-variables.
Test Conclusions of the First Hypothesis
For the first hypothesis, H0 and H1 will be as:
H0: information asymmetry does not have significant effect on financial flexibility
of corporations.
H1: information asymmetry has significant effect on financial flexibility of corporations.
Regression model for the research first hypothesis will be as:
FFit = α0 + β1 BASit + β2
RISKit + β3 BASit*RISKit + β4
CSit +β5 GO it
Received conclusions of this test will be as:
Table 3: test conclusions of the first hypothesis
|
Variable name
|
Variable symbol
|
Coefficient
|
Standard deviation
|
t statistic
|
Prob.
|
Result
|
|
Fixed amount
|
C
|
0.528
|
0.418
|
1.264
|
0.0001
|
meaningful
|
|
Information asymmetry
|
)1βBAS)
|
-0.099
|
0.046
|
-2.137
|
0.0024
|
meaningful
|
|
Corporation size
|
β4 (CS)
|
0.443
|
0.110
|
4.027
|
0.2451
|
Lack of meaningful
|
|
Growth opportunity
|
β5 (GO)
|
0.092
|
0.049
|
1.875
|
0.0452
|
meaningful
|
|
F statistic
Meaningful level (Prob.)
|
|
38.231
0.000
|
|
Watson-Durbin statistic
|
|
2.139
|
|
Determination coefficient (R2)
Adjusted determination coefficient (Adj R2)
|
|
0.479
0.432
|
Test Result
Based on the test conclusions of the research first model, level of significance
of statistic (0.000) is less than error level and total regression model is significant.
Watson-Durbin statistic (2.139) is in region from 1.5 to 2.5. So, correlation doesn`t
exist between model error members. The value of t is significant (p<0.05) and
due to negative value for β1 coefficient, the test conclusions indicate that information
asymmetry has negative significant effect on financial flexibility, so H0 of the
research can be rejected in 5 percent error level. Moreover, t statistic of the
accepted error level for β2 of this test conclusion indicates that controlling variable
of corporation size does not have meaningful relationship with flexibility and t
statistic of the accepted error level for β5 of this test conclusion indicates controlling
variable of corporation growth opportunity has positive meaningful relationship
with flexibility. Determination coefficient and adjusted determination coefficient
indicate that entered variables in regression can explain 43 percent of dependent
variable changes.
Conclusion
Based on the results received from the tests, it can be concluded that information
asymmetry has negative yet significant effect on financial flexibility in 5 percent
error level. Controlling variable of corporation size has no meaningful relationship
with financial flexibility and growth opportunity variable has positive meaningful
relationship with financial flexibility. Research estimated variable will be as:
FFit= 0.528-0.099BAS+0.443CS+0.092Go
Test Conclusions of the Second Hypothesis
For the first hypothesis, H0 and H1 will be as:
H0: liquidity risk does not have significant effect on financial flexibility of
corporations.
H1: liquidity risk has signifiant effect on financial flexibility of corporations.
Regression model for the research second hypothesis will be as:
FFit = α0 + β1 BASit + β2
RISKit + β3 BASit*RISKit + β4
CSit +β5 GO it
Received conclusions of this test will be as:
Table 4: test conclusions of the second hypothesis
|
Variable name
|
Variable symbol
|
Coefficient
|
Standard deviation
|
t statistic
|
Prob.
|
Result
|
|
Fixed amount
|
C
|
0.528
|
0.418
|
1.264
|
0.0001
|
meaningful
|
|
Liquidity risk of stock
|
β2(Risk)
|
0.637
|
0.148
|
4.291
|
0.0057
|
meaningful
|
|
Corporation size
|
β4(CS)
|
0.443
|
0.110
|
4.027
|
0.2451
|
Lack of meaningful
|
|
Growth opportunity
|
β5 (GO)
|
0.092
|
0.049
|
1.875
|
0.0452
|
meaningful
|
|
F statistic
Meaningful level (Prob.)
|
|
38.231
0.000
|
|
Watson-Durbin statistic
|
|
2.139
|
|
Determination coefficient (R2)
Adjusted determination coefficient (Adj R2)
|
|
0.479
0.432
|
Test Result
Based on the test conclusions of the research second model, level of significance
of statistic (0.000) is less than error level and total regression model is meaningful.
Watson-Durbin statistic (2.139) is in region from 1.5 to 2.5. So, correlation doesn`t
exist between model error members. As the t statistics is lower than p value and
due to negative value for β1 coefficient, the test conclusions indicate that liquidity
risk has positive meaningful effect on financial flexibility, so H0 of the research
can be rejected in 5 percent error level. Moreover, t statistic of the accepted
error level for β4 of this test conclusion indicates that controlling variable of
corporation size does not have significant relationship with flexibility and t statistic
of the accepted error level for β5 of this test conclusion indicates controlling
variable of corporation growth opportunity has positive meaningful relationship
with flexibility. Determination coefficient and adjusted determination coefficient
indicate that entered variables in regression can explain 43 percent of dependent
variable changes.
Conclusion
Based on the received conclusions of the test, it can be concluded that liquidity
risk of stock has meaningful effect on financial flexibility in 5 percent error
level. Controlling variable of corporation size has no meaningful relationship with
financial flexibility and growth opportunity variable has positive meaningful relationship
with financial flexibility. Research estimated variable will be as:
FFit= 0.528+ 0.637RISK+0.443CS+0.092Go
Test Conclusions of the Third Hypothesis
For the first hypothesis, H0 and H1 will be as:
H0: information asymmetry and liquidity risk do not have significant effect on financial
flexibility of corporations.
H1: information asymmetry and liquidity risk have significant effect on financial
flexibility of corporations.
Regression model for the research third hypothesis will be as:
FFit = α0 + β1 BASit + β2
RISKit + β3 BASit*RISKit + β4
CSit +β5 GO it
Received conclusions of this test will be as:
Table 5: test conclusions of the second hypothesis
|
Variable name
|
Variable symbol
|
Coefficient
|
Standard deviation
|
t statistic
|
Prob.
|
Result
|
|
Fixed amount
|
C
|
0.528
|
0.418
|
1.264
|
0.0001
|
meaningful
|
|
Liquidity risk of stock
|
β2(Risk)
|
0.637
|
0.148
|
4.291
|
0.0057
|
meaningful
|
|
Information asymmetry
|
β2(BAS)
|
-0.99
|
0.046
|
-2.137
|
0.0024
|
meaningful
|
|
Information symmetry* Risk
|
β3(BAS*Risk)
|
-0.167
|
0.037
|
-4.522
|
0.0328
|
Meaningful
|
|
Corporation size
|
β4(CS)
|
0.443
|
0.110
|
4.027
|
0.2451
|
Lack of meaningful
|
|
Growth opportunity
|
β5 (GO)
|
0.092
|
0.049
|
1.875
|
0.0452
|
meaningful
|
|
F statistic
Meaningful level (Prob.)
|
|
38.231
0.000
|
|
Watson-Durbin statistic
|
|
2.139
|
|
Determination coefficient (R2)
Adjusted determination coefficient (Adj R2)
|
|
0.479
0.432
|
Test Result
Based on the test conclusions of the research second model, meaningful level of
statistic (0.000) is less than error level and total regression model is meaningful.
Watson-Durbin statistic (2.139) is in region from 1.5 to 2.5. So, correlation doesn`t
exist between model error members. The value of t is significant (p<0.05) and
due to negative value for β1 coefficient, the test conclusions indicate that liquidity
risk and information asymmetry have negative significant effect on financial flexibility,
so H0 of the research can be rejected at 5 percent level of significance. Moreover,
t statistic of the accepted error level for β4 of this test conclusions indicates
that controlling variable of corporation size does not have meaningful relationship
with flexibility and t statistic of the accepted error level for β5 of this test
conclusions indicates controlling variable of corporation growth opportunity has
positive meaningful relationship with flexibility. Determination coefficient and
adjusted determination coefficient indicate that entered variables in regression
can explain 43 percent of dependent variable changes.
Conclusion
Based on the received conclusions of the test, it can be concluded that liquidity
risk of stock has meaningful effect on financial flexibility in 5 percent error
level. Controlling variable of corporation size has no meaningful relationship with
financial flexibility and growth opportunity variable has positive meaningful relationship
with financial flexibility. Research estimated variable will be as:
FFit= 0.528+ 0.637RISK -0.099BAS -0.167BAS*RISK+0.443CS+0.092Go
Table 6: Summery of independent variable effectiveness conclusions on dependent
variables.
|
Dependent variable
|
Financial flexibility
|
|
Result
|
Effect
|
Variables
|
|
Rejection of H0
|
Negative
|
Information asymmetry
|
Independent variables
|
|
Rejection of H0
|
Positive
|
Liquidity risk
|
|
Rejection of H0
|
Negative
|
Asymmetry *Risk
|
Research Findings in Term of Test Division of each of the Hypotheses
First Hypothesis
Based on the research first model test conclusions, meaningful level of statistic
(0.000) is less than error level and total regression model is meaningful. Watson-Durbin
statistic (2.139) is in region from 1.5 to 2.5. So, correlation doesn`t exist between
model error members. The value of t is significant (p<0.05) and due to negative
value for β1 coefficient, the test conclusions indicate that information asymmetry
has negative meaningful effect on financial flexibility, so H0 of the research can
be rejected in 5 percent error level.
On the basis of hypothesis test it can be concluded that information asymmetry has
negative meaningful effect on financial flexibility, it means that the effect of
information asymmetry on financial flexibility is a reversed effect.
As mentioned before in the theoretical bases, information asymmetry occurs when
individuals inside or outside of the corporation access to the information that
other individuals are not aware of. This lack of information balance will cause
information asymmetry. While amount of information asymmetry in stock market is
higher, it will stock sale and buy bids. It means that negative secret information
divulgence will cause stock supply be more and sale bid price be higher and vice
versa. Without information asymmetry, as mentioned before information will increase
domain of sale and buy bid price and will stop retail investors` investments. Otherwise,
demand amount for corporation stock will decrease and finally, stock liquidity will
move down and this function will be followed by corporation access to financial
sources because they can sell less stock. Creditors know stock liquidity amount
of a corporation in Tehran Stock Exchange as they use to evaluate their performances
on regular basis. Based on conclusions of research hypothesis test, it can be concluded
that if information amount increases, corporation access amount to financial sources
will be less and the corporation financial flexibility will decrease. These conclusions
are similar to that of the researches done by Langford & Watts (2008), Behartachia
& et.al. (2008), and Antoniewgpiou & et.al. (2011). Moreover, this research
hypothesis conclusions will be correlated to the Iranian done researches by Khodarahmi
& et.al. (2015), Saghafi & et.al. (2013), and Khodamipoor & et.al. (2012).
Second Hypothesis
Based on the test conclusions of the research second model, meaningful level of
statistic (0.000) is less than error level and total regression model is meaningful.
Watson-Durbin statistic (2.139) is in region from 1.5 to 2.5. So, correlation doesn`t
exist between model error members. The value of t is significant (p<0.05) and
due to negative value for β1 coefficient, the test conclusions indicate that liquidity
risk has positive meaningful effect on financial flexibility, so H0 of the research
can be rejected in 5 percent error level.
Received conclusion of this hypothesis test indicates increase liquidity risk of
stock will be followed by increase of corporation financial flexibility. It means
the direct effect of liquidity risk on financial flexibility. Based on research
theoretical bases, it is expected logically that with danger increase amount of
lack of stock liquidity, corporation stock demand, corporation financial access
amount and corporation financial flexibility will decrease. However, this hypothesis
result can be proved for another subject. It can be expressed as; corporations that
have been run or corporations whose stocks don`t have high liquidity in stock exchange
are more conservatism corporations, it means that they will avoid investment opportunities
or postpone unnecessary payments because they can reserve their financial sources
to pay and react for necessary and suddenly payments immediately. So, it can be
said that, corporations that are aware of high risk of their stock liquidity, will
reserve more amount of cash flow to have sufficient financial sources for their
necessary payments, so this approach expresses that liquidity risk of high stock
can increase amount of cash low reservation by corporations` financial managers
and this function will increase amount of corporation financial flexibility.
This research hypothesis conclusions are against the researches done by, Skoobin
& Wan Hool (2010), and Arsalan & et.al. (2010), moreover; they are against
the researches done in Iran such as; Habibisamar & et.al. (2014), while these
conclusions are correlated with the researches done by Falahshams & Hashemei,
(2015).
Third Hypothesis
Based on the test conclusions of the research second model, meaningful level of
statistic (0.000) is less than error level and total regression model is meaningful.
Watson-Durbin statistic (2.139) will be in this distance from 1.5 to 2.5. So, correlation
doesn`t exist between model error members. Based on lowering of t statistic of P-Value
from acceptance error level 5 percent and in attention to negative amount of t statistic
for β3 coefficient, the test conclusions indicate that liquidity risk and information
asymmetry have negative meaningful effect on financial flexibility, so H0 of the
research can be rejected in 5 percent error level.
Based on the received conclusions of this research hypothesis, it can be expressed
that if amount of stock liquidity risk stock with information asymmetry of a corporation
increase, corporation access amount to financial sources will be less and finally,
corporation financial flexibility will decrease. It means that lack of information
asymmetry with stock liquidity risk will decrease corporation financial flexibility.
When a corporation will be encountered with gap in demand and supply because of
lack of suitable information divulgence. The mentioned subject will decrease usual
shareholders` demands to buy their stocks and this factor will make corporation
stock liquidity risk goes higher and it will be followed by corporation access decrease
to external financial sources and they should use internal financial sources such
as; conserved profit or partners` suggested profits to supply financial part of
their corporations. In this situation, corporation will face with financial limitation
that have direct effect on lack of corporation financial flexibility.
Conclusion
Based on the received conclusions of the research three hypotheses it can be concluded
that increase lack of information asymmetry will create obstacle from corporation
stock buy for public and only individual who access to secret information will benefit
and it result will cause that investors will encounter with decrease of the values
of their stocks. Because domain of buy and sale bid price will increase and corporation
stock liquidity will be less and it is a reason for increase of corporation financial
limitation amount and decrease of corporation financial flexibility. However, corporations
that without lack of information asymmetry their sale and buy are high can because
of other reasons such as; new running corporation or systematic risk of inflation,
downturn or barriers for ingredient import from outside of the country can be reasons
for high risk of corporation stock. In these situations corporations can store their
cash flows in attention to their stock liquidity risks to use them in time of sudden
payments to have answer ability to these situations. So, they will be in high level
in term of financial flexibility. Finally, a corporation that has both information
asymmetry and high stock liquidity risk it is expected logically that corporation
access amount to financial sources will decrease not only by stock sale but also
by financial supplement such as; loan and this function will be the result of high
financial limitation and decrease of corporation financial flexibility.
Suggestions from Test Conclusions of Hypotheses
1) In consideration to the first hypothesis conclusions, it can be said that lack
of information asymmetry has negative effects for corporation investors and this
factor only benefit will be for the individuals who access secret information. This
research hypothesis indicates that if lack of information asymmetry increases, corporation
financial flexibility will be less. By considering this factor it is suggested that
managers should stop existing lack of information asymmetry because it will cause
endangering of stock liquidity in stock exchange market. The main sources of this
subject can cause suitable internal control creations with information suitable
divulgence that cause misuses of organization internal individuals. With decrease
of lack of information asymmetry amount, it can be expected that corporation stock
will have higher demand in market and stock liquidity amount will increase. Moreover,
it is suggested that investors in stock exchange should consider structure of corporation
guideline system such as, presents of institutional investors in mixture of investors
and presents of irresponsible members in the board mixture and competition status
in product market. In addition to, corporations whose stock have been transacted
by investigating financial statements of the previous durations conclude that their
information divulgence amount will be suitable and will cause barriers for lack
of information asymmetry.
2) Based on the received conclusions of the second hypothesis, liquidity risk amount
will increase corporation financial flexibility amount. It is suggested that financial
managers should consider other suitable ways to increase their financial flexibility
amount in spite of cash flow storage such as; financial leverage increase as same
as suitable size of corporation payment ability, correctness of corporation capital
structure and investment in the projects with less risks. Cash flow storage can
increase corporation financial flexibility; however, it will cause barrier for the
corporation use of profitable opportunities. So, it is suggested that cash flow
storage should be for contrast of stock liquidity risk in the acceptable and suitable
level to the corporation capacity. Moreover, it is suggested that investors in stock
exchange shouldn`t know financial flexibility and on time payment of stock profit
as their stock choice criterions because it may be that financial flexibility will
be the result of high cash flow storage and high risk of lack of stock liquidity
and these reasons can`t be valuable for the corporation profitability.
3) Finally, third hypothesis conclusion indicates that information asymmetry and
liquidity risk together can stop corporation financial flexibility increase and
they will decrease corporation financial ability. So, it is suggested that mangers
should make appropriate decisions to decrease information asymmetry and stock liquidity
risk such as; suitable divulgence, financial structure correctness, suitable financial
supplement, investment in profitable projects, decrease of unsuitable storage of
cash flow and other similar functions. Because they can decrease domain difference
of buy and sale bid price and decrease stock liquidity risk, so corporation accesses
to financial sources easily and own more financial flexibility. In addition to,
it is suggested to creditors and banks that corporation should have appropriate
performance of information suitable divulgence during previous durations for giving
loans and credits and corporations should have information suitable divulgence amount.
It is suggested that investors should invest in the corporations that have less
stock liquidity risk and existence of liability in balance sheet can`t be reason
for the corporation weakness. It should be clarified that financial supplement have
been for what purposes and it is not the only negative factor for investments in
the projects but it can increase relative corporation stock value. So, not only
mentioned factors but also financial flexibility should be considered.
References
- Bagherbaigi, M., Pooralikelayeh. M.R., Armin, A. (2011), “Investigating relationship
between financial flexibility with growth situations and future value of the accepted
corporations in Tehran Stock Exchange”, The First Meeting of Management Discussion
Gradation Solutions, Accounting & Industrial Engineering in Organizations
- Habibisamar, J., Tehrani, R., Ansari, K. (2014), “Investigating relationship between
liquidity risk and market risk with valuing and growing stock return of AHP in Tehran
Stock Exchange”, Magazine of Stock Exchange Management & Financial Engineering,
No. 23, p.p. 39-58
- Khodarahmi, B., Foroghnezhad, H., Sharifi, M.J., Talebi, A.R. (2015), “The effect
of information asymmetry on future downturn risk of stock price in the accepted
corporation of Tehran Stock Exchange”, Researching & Scientific Quarterly of
Property Management & Financial Supplement, 4 th Year, No. 3, p.p.
39-58
- Khodaeivalehzaghrad, M., Raretaimoori, M. (2009), “The effect of financial flexibility
on investment decisions”, Magazine of Financial Management & Financial Portfolio
Management, No. 3, p.p. 155-173
- Shaerianaghizh, S., Bolo, Gh., Mohsenimalekirastaghi, B. (2015), “Relationship
between financial flexibility and financial supplement kind in the accepted corporation
of Tehran Stock Exchange”, 6th year, No. 22, p.p. 171-190
- Ghaemi, M.H., Vatanparast. M.R. (2004), “Investigating accounting information
role in decrease of information asymmetry in Tehran Stock Exchange”, Investigations
of Accounting and Auditing, 12th Year, No. 41, p.p.85-103
-Vakilirfard, H.R., Rostami, V. (2009), “Analysis of information asymmetry gap domain
between profession members, producers, and users of accounting information based
on qualitative accounting information and financial reporting”, Management Accounting,
3rd Duration, No. 6, p.p. 25-39
-Amihud, Y. (2002) Illiquidity and Stock Returns: Cross – Section and Time Series
Effects, Journal of Financial Markets5, PP. 31–56.
-Bonaime, A. A., Hankins, K. W., & Jordan, B. D (2016). "The cost of financial
flexibility: Evidence from share repurchases". S0929-1199(16) 30018-9, pp. 1-50.
-Chan, J. S. P., Hong, D., & Subrahmanyan, M. G. (2007)." A tale of two prices:
Liquidity and asset prices in multiple market". Journal of Banking &Finance,
Vol. 32, pp 947-960.
-De La Bruslerie, Hubert and Latrous Imen. (2014). Ownership Structure and Debt
Leverage: Empirical Test of a Trade-off Hypothesis on French Firms. Journal of Multinational
Financial Management, 22 (4): PP.111-130.
-Martinez, A., & Miguel, N. B (2005). "Asset pricing and liquidity risk: A empirical
investigation of the Spanish stock market". International Review of Economics and
Finance 14, 81–103.
-Myers, S. and Majluf, N. (1984). Corporate financing and investmentdecisions when
firms have information that investors do not have. Journal Finance Economic , 13,
187–221.
-Pastor, L., & Stambaugh, R. (2003)." Liquidity risk and expected stock returns".
Journal of Political Economy 111, 642–685.
-Piqueira, N (2006). "Trading activity, illiquidity costs and stock returns, working
paper". Princeton University, Social Science ElectronicPublishing, Inc.
-Venkatesh, P. C., and R. Chiang, (1986) “Information Asymmetry andthe Dealers Bid-
Ask Spread: A Case Study of Earnings and Dividend Announcements ".The Journal of
Finance,Vol.41,No.5,pp 1089-1102.