|
Mahamudul Hasan Lecturer Department of Marketing Faculty of Business Administration and Management Patuakhali Science and Technology University (PSTU) E-mail:- tuhinjobs46@gmail.com |
Md. Rasel Sheikh BBA (Major in Marketing) Patuakhali Science and Technology University MBA (Major in Marketing),Khulna University E-mail:- rasels734@gmail.com |
This paper aims to identify and analyze the factors that affect the attitude toward social marketing which are run by social media. The researchers have conducted a survey on 201 undergraduate students from three public universities from southern regions of Bangladesh. At first the researchers have tested the reliability and validity of the measurement through cronbach’s alpha value, factor loading, composite reliability and Average variance extraction. Then the researchers have conducted Regression analysis to test the hypothesis of the study. The results show that ‘Social media use’ and ‘perception of reliability on Social media’ have significant positive impact on attitude toward social marketing through social media. However, ‘following social media’ and ‘concern for privacy on social media’ show no significant impact. The study also showed that attitude toward social marketing through social media has significant positive impact on ‘Being affected by social marketing campaigns through social media’.
Keywords: Social Marketing, Social Media, Attitude, Bangladesh.
Social media marketing has become an important tool for modern Integrated Marketing communication campaigns. The users of various social media platforms are increasing rapidly and the marketers are developing strategic initiatives with significant importance to reach those users through social media marketing techniques. In 2019, it is estimated that there will be around 2.77 billion social media users around the globe, up from 2.46 billion in 2017 (Statista, 2017). With the rapid diffusion of Smartphone and internet in developing countries the number of social media users has reached a large portion and marketers are trying to develop marketing initiatives through social media platforms to reach those target audience. A recent study of ‘We Are Social and Hootsuit’ on the number of social media users has shown that the highest number of social media users reside in Bangkok (capital city in Thailand) and second highest is in Dhaka (capital city in Bangladesh). The Bangladesh capital has 22 million active Facebook users, which is 1.1 percent of the total monthly active users of the social networking site across the globe. These statistics specify the growing importance of social media to spread message among the population whether the message is commercial or cause specific.
For the past few decades, Bangladesh has experienced the application of social marketing in a diverse range of issues. More and more social organisations, government organisations and commercial enterprises are utilising social marketing programs, concepts and tools to solve myriad social problems which were foreseen by Kotler in 1980 (Hasan, 2016 ;Fox and Kotler, 1980). Behavioural development in sanitation, hygiene and safe water use in Bangladesh has been successful through communication and social mobilisation (Bajracharya, 2013). Bangladesh has achieved remarkable progress in social development indicators by conducting the public campaigns (immunisation campaigns) or social marketing campaigns (contraceptive marketing) outside the established structure of service delivery and also by involving the NGOs (Mahmud et al, 2013).
Numerous studies have been conducted to investigate the factors affecting attitude toward social media marketing (Akar & Topcu, 2011; Shiau & Lu, 2010; Cha, 2009; miller & Lammas,2010). However, those studies have focused on social media marketing by commercial firms. None of these studies has focused on factors affecting attitude toward social marketing through social media. Thus, the present study has tried to fill up this research gap by answering the following research questions: What factors affect attitude toward social marketing through social media? How attitude toward social marketing on social media affect Being affected by social marketing? Are there any significant factors that affect attitude toward social marketing through social media than others? If there are factors which affect social marketing through social media than what is the implications for academicians and practitioners of social marketing discipline?
Social Media began when the Internet came into being. Back in 1979, UseNet‟s were used to post articles to newsgroups. Later on, there was the Bulletin Board System (BBS) that was accessible on personal computers though only one person could use it to interact with another individual. (―History and Evolution of Social Media‖, 2009). Social Media is a ―group of internet-based applications that build on the ideological and technological foundations of Web 2.0, and that allow the creation and exchange of user generated content (Kaplan and Haenlein, 2010, p. 61). Social media takes a variety of forms such as social networking sites, content communities, blogs, digital storytelling, image and video sharing, podcast portals, and virtual gaming world. (Kaplan & Haenlein 2010). Sites such as Google, Wikipedia, and Friendster among others were then created. At the moment, they are many with the most popular being Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, LinkedIn, Wikipedia, and Flickr among many others (―History and Evolution of Social Media‖,2009).
Social marketing is the design, implementation, and control of programs calculated to influence the acceptability of social ideas and involving considerations of product planning, pricing, communication, distribution, and marketing research. (Kotler and Zaltman, 1971). Andreasen (1995) developed an updated definition of social marketing to further clarify the concept. He states: ―Social marketing is the application of commercial marketing technologies to the analysis, planning, execution, and evaluation of programs designed to influence the voluntary behavior of target audiences in order to improve their personal welfare and that of the society of which they are a part. The systematic application of marketing alongside other concepts and techniques, to achieve specific behavioral goals, for a social or public good‘ French. (Blair-Stevens, 2006). Kotler and Lee (2008) stated that Social marketing is a process that applies marketing principles and techniques to create, communicate, and deliver value in order to influence target audience behaviors that benefit society (public health, safety, the environment, and communities) as well as the target audience.
The term social marketing is very rare in the existing literatures of Bangladesh. Various scholars and corporate authors have replaced this term with behaviour change communication, public awareness campaign, social mobilisation campaigns, social development campaigns etc (Hasan, 2016).
Rahman and Khan (2008) argued that social marketing in Bangladesh has become a model of best practices and attracted international attention. Two premier US-based graduate schools of business included the case study on social marketing program in Bangladesh in their curricula.Asadullah et al. (2014) noted that changes in selected social development indicators coincided with the timing of social marketing interventions. For instance, diarrhea accounted for one-third of all childhood deaths in the 1970s and 1980s, while another third was attributable to six immunisable diseases. BRAC responded by scaling up the Oral Therapy Extension Program (OTEP) which provided oral rehydration solution using an incomplete but simple substitute (Chowdhuryand Cash, 1998).
Social media marketing is a process that allows individuals to present their own Web sites, products, or services through online social channels to communicate in a wide community and to listen to that community—which is not possible with traditional advertising channels (Weinberg 2009, 3).Social media marketing uses social media sites in order to increase a company‘s or organization‘s visibility on the Internet for the purpose of presenting its products and services. Social media sites are beneficial for creating social (and work) networks and for exchanging thoughts and information (Ontario, 2008).Marketing with social media is making a significant impact on the marketing strategies of companies. This kind of marketing is gradually rising, expanding, and taking the place of older methods in some companies. Social media marketing consists of multidirectional dialogs and it is participatory and often user generated. (Awareness 2008b). Social media marketing can be simply defined as the use of social media channels to promote a company and its products. This kind of marketing can be thought of as a subset of online marketing activities that complete traditional Web-based promotion strategies, such as e-mail newsletters and online advertising campaigns (Barefoot and Szabo 2010, 13).
According to Kotler and Keller (2006, 194), attitude can be described as ‗‗a person‘s enduring favorable or unfavorable evaluation, emotional feeling, and action tendencies toward some object or idea.The better the attitude a person has toward a brand, the more likely he or she is to use the product. Conversely, the less positive the attitude, the less likely he or she would be to use the product (Chiou et al. 2008). Miller and Lammas (2010) stated that the expectations that marketing with social media applications can cause tremendously effective marketing are very high. An iProspect (2007) report stated that social networking sites affect purchasing decisions of a meaningful percentage of Internet users visiting these sites. In this context, it is required that marketers identify the sites in which the influence level is high. Also, they can develop methods to have a close relationship with users who visit these sites (iProspect 2007).
Akar and Topcu ( 2011) noted several factors that affect attitude toward social media marketing. These are Social media use, social media knowledge, following/monitoring social media, foresight about social media, fear about social media. The impact of attitude toward social media marketing on Being affected by social media marketing has also been analyzed in the study. Buskens, (2002) stated that trust or reliability is much important to draw people toward social sites. Consumers are wary of propaganda that is spread in the social media. If some social networking sites are regarded unreliable then advertising in such sites will not achieve the marketing rationale or objective that is sought. Sarwar et al. (2013) has noted that interaction on social networking sites and the perception on the reliability on social networking advertising have significant impact on purchase intention of consumers.
Hypothesis
H1: Social media use has significant impact on attitude toward social media campaign through social media.
H2: Following/monitoring social media has significant impact on attitude toward social media campaign through social media.
H3: Concern for privacy using social media has significant impact on attitude toward social media campaign through social media.
H4: Perception toward reliability of social marketing campaign through social media has significant impact on attitude toward social media campaign through social media.
H5: Attitude toward social media campaign through social media has significant impact on being affected by internet and social media.
Conceptual Framework
Figure 1
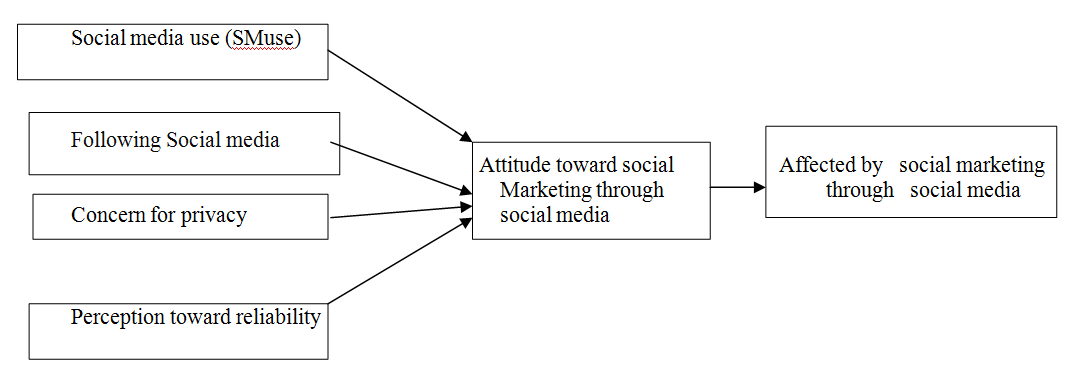
Figure -1 exhibits the conceptual framework of the study according to the hypothesis and objectives of the hypotheses. Figure -1 shows that social media use, following social media, concern for privacy in social media and perception toward reliability toward social media have direct impact on Attitude toward social marketing through social media. The attitude toward social Marketing through social Media also has direct impact being Affected by social marketing through Social media.
Survey and Data Collection
The study is descriptive research and quantitative in nature. The sample of the study is comprised of the undergraduate students of Khulna University of Engineering and Technology, University of Khulna and Patuakhali Science and Technology University. The information was collected directly from field survey by a structured questionnaire from January 24 to February 20, 2017. The final responses that were received after excluding the missing and incomplete responses were 201.
Instruments and Measures
The scale items were identified using extensive literature review. Measures of other variables are adopted from previous studies that validated the respective scales. Measurement of Attitude toward social marketing through Social media, Being affected by internet and social media , Following/monitoring social media have been adapted from Akar and Topcu (2011). In order to measure the concern for privacy in social media we adopted the measurement used by Simona et al.(2013). The measurements of perception on the reliability of online advertisement in social media have been adapted from Sarwar and Haque et al. (2013).
Data Analysis:
The statistical package SPSS (version 23.0) has been used for data analysis. First, the demographic characteristics of the respondents have been presented through frequency table. Second, The Reliability and validity of the questionnaire have been checked through Cronbach’s Alpha value, factor loading, average variance extracted and composite reliability, ; second, Multiple regression analysis has been performed to understand the impact of Social media use, following social media, using social media, concern for privacy and perception toward reliability on social marketing through social media on the attitude toward social marketing through social media. ; third, Bivariate regression analysis has been performed to understand the impact of attitude toward social media on Being affected by social media.
Out of 201 respondents, 150 were male and 51 were female. Moreover, all of the respondents are undergraduate students. 50 respondents spend 1-4 hours in social media, 59 respondents spend 5-8 hours and 92 respondents spend more than 8 hours in social media weekly.
Table -1
|
Variable |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
Gender |
||
|
Male |
150 |
0.746% |
|
Female |
51 |
0.256% |
|
Total |
201 |
|
|
Educational Qualifications |
||
|
Undergraduate students of 3 public Universities |
201 |
100% |
|
Time spent on Social Media Weekly |
||
|
1-4 hours |
50 |
0.248% |
|
5-8 hours |
59 |
0.294% |
|
More than 8 hours |
92 |
0.456% |
|
Total |
201 |
Reliability and Validity Analysis
Table 2: Results of Reliability and Validity Tests
|
Constructs |
Statements |
Cronb |
Composite |
Factor |
Average |
||||
|
-ach’s |
Reliability |
Loading |
Variance |
||||||
|
Alpha |
Extracted |
||||||||
|
It is necessary to use social media for |
.769 |
||||||||
|
Attitude toward social |
through social media. |
creating awareness about social issues |
|||||||
|
marketing campaign |
It is a good idea to create public |
||||||||
|
awareness about social issues through |
.858 |
||||||||
|
social media. |
|||||||||
|
It is useful to create public awareness |
.758 |
0.770891 |
.785 |
0.575938 |
|||||
|
about social issues through social media |
|||||||||
|
I like the Facebook page and You Tube |
|||||||||
|
videos that are developed for creating |
.600 |
||||||||
|
awareness regarding social media. |
|||||||||
|
use |
I use social networking sites such as |
.744 |
|||||||
|
Facebook regularly. |
|||||||||
|
media |
I like using applications such as YouTube, |
||||||||
|
Facebook, and blogs, generally known as |
.609 |
0.724209 |
.682 |
0.4681 |
|||||
|
social media |
|||||||||
|
Social |
|||||||||
|
I use video sharing sites such as YouTube |
.621 |
||||||||
|
regularly |
|||||||||
|
affected by |
internet and |
social media |
Public awareness activities conducted by |
.697 |
|||||
|
social media affect my thinking. |
|||||||||
|
Being |
Advertisement on social problems on |
.612 |
0.690688 |
0.527917 |
|||||
|
internet increase my knowledge on that |
.755 |
||||||||
|
issue |
|||||||||
|
Following/ |
Monitoring |
I follow wikis such as Wikipedia regularly |
.788 |
||||||
|
g social |
media |
I follow blog sites regularly |
.767 |
||||||
|
I follow Facebook regularly |
.712 |
0.689379 |
.698 |
0.51744 |
|||||
|
I follow You Tube regularly |
.611 |
||||||||
|
privacy using |
I am concerned regarding the |
||||||||
|
Concern for |
social media |
confidentiality of my personal information |
.866 |
||||||
|
in Facebook. |
|||||||||
|
Social media does not endanger my |
.25 |
0.707707 |
0.555579 |
||||||
|
privacy |
.601 |
||||||||
|
marketing campaign |
through social media |
I trust the publicity made on social issues |
.706 |
||||||
|
Perception toward |
reliability of social |
on social network. |
|||||||
|
I am satisfied with the information that I |
.744 |
||||||||
|
have found from social media |
.669 |
0.761592 |
0.515863 |
||||||
|
I join a group in social networking for |
|||||||||
|
various updates |
.704 |
||||||||
Cronbach‘s coefficient alpha, which measures how well the variables positively relate to one another, was generated by using SPSS software. (Y. Saleem, M.R. Kamran, F. Sabir & J. Iqbal, 2013). The reliability is measured by calculating Cronbatch Alpha and the value ranges from .6 to .9. Table 2 shows that attitude toward social marketing campaign through social media has Cronbach‘s Alpha .758 and composite reliability .770, Social media use has Cronbach‘s Alpha .690 and composite reliability .724, Being affected by internet and social media has Cronbach‘s Alpha .612 and composite reliability .690, Following/monitoring social media has Cronbach‘s Alpha .712 composite reliability .689, Concern for privacy using social media has Cronbach‘s Alpha .25 and composite reliability .707 (though Cronbach‘s Alpha is lower bounded here but composite reliability gave a a significant reliable value as an alternative of Cronbach‘s Alpha), Perception toward reliability of social marketing campaign through social media has Cronbach‘s Alpha .669 and composite reliability .761 which are considered reliable for the study.
All constructs had values of AVE larger than 0.5, indicating that they met the acceptable standard of convergent validity (Barclay et al., 1995).Each factors has more than .50 AVE value except social media use. Though it has less than .5 AVE value but it has strong Cronbach‘s Alpha and composite reliability value. That is why this factor is also considered for analysis
Hypothesis Testing
Table- 3
|
Model 1 |
Sum of |
df |
Mean |
F |
Sig. |
||
|
Squares |
Square |
||||||
|
Regression |
10.796 |
5 |
2.159 |
5.429 |
.000a |
||
|
Residual |
77.556 |
195 |
.398 |
||||
|
Total |
88.351 |
200 |
a. Predictors: (Constant), SMuse, Following, Experience, Privacy, Reliability
b. Dependent Variable: Attitude
Table 3 shows that the F value
Table- 4
Regression Coefficient
|
Beta |
||||
|
Factors |
coefficient |
t |
Sig. |
|
|
(Constant) |
2.782 |
7.831 |
.000 |
|
|
SMuse |
.158 |
2.256 |
.025 |
|
|
Following social media |
.029 |
.423 |
.673 |
|
|
Privacy |
.006 |
.117 |
.907 |
|
|
Reliability |
.220 |
3.888 |
.000 |
Test of Hypothesis 1 to 4
Table 3 shows the ANOVA table of the regression model which has been used to test the first 5 hypothesis of the study. The F value is 5.429 which is significant at 0.05 significance level. Therefore, the factors of the study have significant impact on the attitude toward social marketing through social media.
Table 4 shows the regression coefficient values and the significance value of the factors affecting the attitude social marketing through social media. The table shows ‘social media use’ and ‘perception of reliability’ on social marketing through social media have significant positive impact on attitude toward social marketing through social media. Therefore, Hypotheses 1 and Hypotheses 4 have been accepted. However, ‘ following social media’ and ‘ perception of privacy’ on social media have no significant impact on social marketing through social media . Hence, Hypotheses 2 and 3 are not accepted.
Table - 5
|
Model Summary |
||||
|
Model |
R |
R Square |
Adjusted R Square |
Std. Error of the Estimate |
|
1 |
.341a |
.116 |
.112 |
.68090 |
|
a. Predictors: (Constant), attitude |
||||
Table- 6
|
ANOVAa |
||||||
|
Model |
Sum of Squares |
df |
Mean Square |
F |
Sig. |
|
|
1 |
Regression |
12.107 |
1 |
12.107 |
26.114 |
.000b |
|
Residual |
92.261 |
199 |
.464 |
|||
|
Total |
104.368 |
200 |
||||
|
a. Dependent Variable: Being Affected by Social Marketing through Social media |
||||||
|
b. Predictors: (Constant), attitude toward social marketing through social media |
||||||
Table - 7
|
Coefficientsa |
||||||
|
Model |
Unstandardized Coefficients |
Standardized Coefficients |
t |
Sig. |
||
|
B |
Std. Error |
Beta |
||||
|
1 |
(Constant) |
2.178 |
.305 |
7.132 |
.000 |
|
|
attitude |
.370 |
.072 |
.341 |
5.110 |
.000 |
|
|
a. Dependent Variable: Affected |
||||||
Test of Hypothesis 5:
Table 6 shows the F value of the ‘impact of attitude toward social marketing through social media’ on ‘Being Affected by social marketing through social media’ is 26.114 which is significant at 0.05 significance level. Table 6 shows that the regression coefficient of ‘Attitude toward Social Marketing through Social Media’ on ‘ Being Affected by social marketing through social media is also significant at 0.05 significance level. Therefore, the Hypothesis 5 that there is a significant impact of ‘Attitude toward social marketing through social media’ on ‘being Affected by social marketing through social media ‘ is accepted.
The aim of the study was to identify and analyze the factors that affect the attitude toward social marketing through social media and to analyze the impact of attitude toward social marketing through social media on ‘Being affected by Social marketing through Social Media’.
The results of the study show that ‘social Media usage’ and the’ perception of reliability’ have significant impact on the Attitude toward Social Marketing through Social Media’. This indicates that the regular users of social media have positive attitude toward social marketing campaigns and advertisements on social media. Therefore, social marketing campaigners should develop user friendly, interactive , informative contents and messages in social media to target the regular users of social media. With the increasing prevalence and popularity of internet and social media sites the number of users of social media is increasing continuously. Hence, during the development of IMC campaigns for any social marketing idea special attention should be given on social media marketing part to reach a wide number target audience.
The results shows that ‘perception toward reliability on social marketing through social media’ has significant impact on the Attitude toward social marketing through social media. Therefore, the social marketing campaigns, messages and contents in social media should be reliable and reflect original scenario. Emphasizing on too much fear or humour on social marketing message or exaggeration of the real scenario may make the social marketing cause less reliable to the target audience.
The results of the study show that ‘Following Social Media’ has no significant impact on the ‘attitude toward social marketing through Social media’ that is consistent with the findings of Akar & Topcu (2011) . One explanation may be that the study of Akar and topcu (2011) identified the factors affect the attitude toward social media marketing which was mainly based on conventional commercial marketing whereas the present study is based specifically on social marketing in social media.
‘Concern for privacy in social media’ has no significant impact on ‘attitude toward social marketing in social media’ (p>0.907). The reasonable explanation is that social media users may consider privacy and security an essential factor but the recent improvements and customizations in social media privacy and security have made it a factor that’s absence may cause serious problem but presence doesn’t cause any significant contribution toward the formation of positive attitude.
‘Attitude toward social marketing through social media ‘on ‘Being affected by social marketing through social media’ is significant (p<0.05). This indicates that attitude toward social marketing through social media has direct significant impact on target audience. Hence, social marketing campaigners must try hard to develop positive attitude toward social marketing campaigns through social media by focusing on factors which are crucial to increase attitude toward social marketing through social media.
The study has been conducted on 201 respondents on 3 public universities of Bangladesh. To generalize the study the study should be replicated on much larger sample. The impact of some important demographic variables which have been found significant in some other studies should be included in future studies e.g. Gender .The study includes only five independent variables and future studies should identify and analyze other independent variables.
Akar, A & Topcu,B. “An Examination of the Factors Influencing Consumers' Attitudes Toward Social Media Marketing”, Journal of Internet Commerce, 10:1, 35-67, DOI: 10.1080/15332861.2011.558456 http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/15332861.2011.558456.
Andreasen, R.A. (1994) ‘Social marketing: its definition and domain’, Journal of Public Policy and
Marketing, Spring, Vol. 13, No. I, pp.108–114.
Asadullah, M.N., Savoia, A. and Mahmud, W. (2014) ‘Paths to development: is there a Bangladesh
surprise?’, World Development , Vol. 62, pp.138–154.
Awareness. (2008b). “Social media marketing: Integrating social media in your marketing mix”.: http://www.awarenessnetworks.com/resources/Integrating-Social- Media.pdf (accessed July 6, 2009).
Barefoot, D., and J. Szabo. (2010). Friends with benefits: A social media marketing handbook. San Francisco: No Starch Press.
Buskens, V. W. (2002). Social networks and trust. Boston, mass: Kluwer Academic
Cha, J. 2009. “Shopping on social networking Web sites: Attitudes toward real versus virtual items”. Journal of Interactive Advertising 10 (1): 77–93.
Hasan, M. (2016) “Social marketing in Bangladesh: status, prospects and barriers”, Int. J.
Society Systems Science, Vol. 8, No. 2, pp.171–184.
https://www.webdesignerdepot.com/2009/10/the-history-and-evolution-of-social-media/ (electronically Accessed on 2nd December, 2017).
https://www.statista.com/statistics/278414/number-of-worldwide-social-network-users/ (electronically accessed on 2nd December, 2017).
iProspect. 2007. iProspect social networking user behavior study. http://www. iprospect.com/premiumPDFs/researchstudy_2007_socialnetworkingbehavior. pdf (accessed December 24, 2010).
Kaplan, A. M., & Haenlein, M. (2010). Users of the world, unite! The challenges and opportunities of social media. Business Horizons,53(1), 59–68.
Kotler P., Lee N. (2008), Social Marketing : Influencing behaviours for Good, Sage Publications, 3rd edition.
Kotler, P., and K. L. Keller. 2006. Marketing management. 12th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Kotler, F. and Zaltman, G. (1971) ‘Social marketing: an approach to planned social change’, Journal of Marketing, Vol. 35, pp.3–12.
Miller, R., and N. Lammas. 2010. Social media and its implications for viral marketing. Asia Pacific Public Relations Journal. 11:1–9.
Nanji, A. (2015). The Most Effective Social Networks for Marketing a Business in 2015 Retrieved May 5, 2016 from: http://www.marketingprofs.com/charts/2015/27718/the-most-effective-social-networks-for-marketing-a-business-in-2015#ixzz45Ghb27Nc .
Ontario. 2008. Social media marketing: Introduction to social media marketing. http:// www.bruce.on.ca/tools/Social_Media_Marketing.pdf (accessed July 8, 2009).
Rahman, M. and Khan, T.U. (2008) Social Marketing: A Success Story in Bangladesh [online]
http://www.smc-bd.org/index.php/page/view/75 (accessed 20 December 2014).
Sarwar, A, Haque,A & Yasmin, F. The Usage of Social Network as a Marketing Tool: Malaysian Muslim Consumers’ Perspective, International Journal of Academic Research in Economics and Management Sciences , January 2013, Vol. 2, No. 1 ISSN: 2226-3624
Shiau, W.-L., and M. M. Lu. 2010. Continuance intention of blog users: The Impact of Perceived Enjoyment and User Involvement. Proceedings PACIS 2010. http:// www.pacis-net.org/file/2010/S20-02.pdf (accessed December 24, 2010).
Weinberg, T. (2009). The new community rules: Marketing on the social web. Sebastopol, CA: O’Reilly Media, Inc