|
Saghar Zarinkamar Ph.D student in Business Management Marketing Orientation Department of Business Management Central Tehran Branch Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran |
Dr. Vahid Reza Mirabi Associate Professor Department of Business Management Central Tehran Branch Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran |
The main purpose of this research is to investigate the factors affecting customer purchasing decision in the sports wear industry based on the marketing mix model. The statistical population is about 2600 people. Random stratified sampling method was used as the sample in this study. A sample with 335 people was obtained using Morgan's table due to the limited population. In this research, after the retrieval of the questionnaires and the one-sample t-test was applied. According to the applied test and normalization of the data, the results were as follows:
1- The product attributes affects the customers’ decision to purchase sportswear in Tehran City.
2- The price offered affects the customers’ decision to purchase sportswear in Tehran City.
3- The place of supply and distribution of goods affects the customers’ decision to purchase sportswear in Tehran City.
4- The advertisements affect the customers’ decision to purchase sportswear in Tehran City.
Keywords : Customers’ Purchase Decision, Sportswear, Marketing Mix Model, Questionnaire Method
Consumer behavior examines all selection and use processes, dropping products, services, experiences and ideas by individuals, groups and organizations in order to meet the needs, and also examines the impacts of these processes on the customer and society (Hawkins et al. 2006, 6). Having an understanding of the consumer and the consumption process has several advantages. These benefits include helping managers’ decision making, providing a cognitive basis through consumers analysis, helping legislation and regulators to lay down rules on the purchase and sale of goods and services and ultimately helping consumers to make decision. In addition, studying consumer behavior can help us understand the factors related to the social sciences that affect human behavior (Moun, and Minor, 2007). Consumer’s decision making is defined as the process which includes various steps such as problem identification, search for solutions, alternatives evaluation, selection of options, and evaluation of selection results. Successful marketing begins with an understanding of why and how consumers behave (Venus, Roosta, Ebrahimi, 83, p. 112). Because consumer behavior is a delicate phenomenon and is not always clear; therefore, their performance as a consumer is not often predictable and not even narrative. As consumers, most of people are not aware of effective external factors of purchasing, as well as their own internal processes that lead to purchasing decisions. In this research, it is examined the factors affecting customer purchasing decisions in the sportswear industry. In the last few decades, companies have faced the most competition. Rapid and constant changes in consumer tastes, saturation of existing markets, advances and increased competition at the national, international and global levels all indicate the fact that survival and growth of companies and organizations can only be achieved through satisfaction of customers and continuous attention to their needs. Understanding the behavior of consumers to meet their needs and desires is not an easy task. In addition, today customers are faced with a wide range of products, brands and prices. Therefore, in order to maintain the growth in the competition, companies need to answer the questions that how and according to what criteria customers decide to purchase a product (Rahim Kohansal, 2003).
The mix of marketing is a collection of marketing tools that the company uses to achieve their goals in the target market. This term refers to a combination of useful elements in market mechanisms and not only provide the ability to use a wide range of elements, but also suggests that integration brings different results with many benefits. Since 1960s, the application of the concept of marketing mix has begun through the Quadruple Classification of P4 created by McCarthy. These elements included product, price, distribution and promotion. Here we are going to examine the factors affecting the purchasing decision of sportswear customers in Tehran city with the marketing mix model.
Various studies have been done on the impact of marketing mix on customer purchases and brand equity, some of which are listed below.
Torabi Nahad (2012), has done a research titled “Factors Affecting the Purchasing Decision of Sporting Goods Consumers Using the Spaldozo Kendal Model”. This research was carried out on consumers over the age of 18 years old in Tabriz City, it was concluded that there is modernism, idealistic and pleasure in the consumers of sports goods in Tabriz City. Also, the most important factor in making purchasing decisions is modesty and modernity. Men were more innovative than women.
Jalali Farahani (2013) in his research titled "The Effect of Selected Marketing Elements on the Brand Value of Water Wave Land Recreation Center" showed that promotion of sales and image of the center affects the brand equity, but prices and promotions do not have a significant effect on brand value (2).
Nezami (2013) by examining the impact of marketing mix in brand equity in ETKA department stores in Tehran City showed that the image of the store, the amount of distribution, advertising and promotion of the sale have a significant effect on the brand's special value (3).
The results of research done by Iranzadeh et al. (2012) titled “The effect of marketing mix on the brand's special value” showed the impact of price and product elements on all aspects of brand equity and two elements of distribution and promotion activities are also factors affecting awareness and mental association of the brand (1).
Also, Sehat et al. (2012), investigating the impact of marketing mixes on the brand value of the Entrepreneur Insurance Company, found that price, company image and sales promotion affect brand equity, but the amount of advertising does not affect brand especial equity (4).
In the foreign research section, the results of the research done by Raj and Arokisami (2012), titled “The effect of marketing mix and customer perceptions on brand loyalty in Malaysia”, showed that the price, store image, distribution, and price increase have a positive and significant effect on brand loyalty (5).
Hang and Serelago (2012) also examined the relationship between brand equity aspects and marketing mixes. The results showed that there is no relationship between brand awareness and brand equity with brand equity as well as brand awareness and brand awareness. But there was a positive relationship between distribution and awareness of the brand and between prices and advertising.
This research was focused on identifying the factors affecting customer purchase decisions in the sportswear industry based on the marketing mix model in Tehran City.
The Research Hypotheses
-The product attributes affects the customers’ decision to purchase sportswear in Tehran City.
-The price offered affects the customers’ decision to purchase sportswear in Tehran City.
-The place of supply and distribution of goods affects the customers’ decision to purchase sportswear in Tehran City.
-The advertisements affect the customers’ decision to purchase sportswear in Tehran City.
The present study was conducted in 2017; it is applied and survey type in terms of research purpose. The statistical population of this research includes all customers of sportswear in Tehran City. The Morgan table is used to determine the sample size, and the available method is used to select the sample.
The statistical population is about 2600 people. The sample of this study is obtained using the random stratified sampling method. The sample of the study includes 335 customers of sportswear in Tehran city by the Morgan table due to the limited community.
The documentary and library information and referring to the statistics and information were used as the data collection tools. Documentary methods are among the methods with non-disturbing and non-response measures. The documentary method is described as a method that is usually used in research on documents and books in historical methods. The use of documents takes place when:
1. The research is historical 2. The research is related to existing phenomena, but the researcher attempts to identify them.
In this research, the questionnaire is used as the data collection tool and the statistical software, especially SPSS software was used as the statistical analysis tool.
The Smirnov Normality Test
The Shapiro-Wilk test or Kolmogorov-Smirnov test were used to ensure that data was normal.
When evaluating the normality of data, we test the zero hypothesis at 5% error level based on the fact that the data distribution is normal. Therefore, if the significance level of the test statistic is greater than 0.05, then there is no reason to rule out the zero-hypothesis based on the fact that the data is normal. Hence in other words, the distribution of data is normal. For statistical tests, the statistical hypotheses are set as follows:
H0: The distribution of data for each variable is normal.
H1: The distribution of data for each variable is not normal.
The results of Kolmogorov-Smirnov's normality test are summarized in the table below.
Table 1. Results of Kolmogorov-Smirnov's Normality Test
|
Items |
Coefficient obtained |
Significance |
Result |
|
Items related to the first hypothesis |
0.13 |
0.24 |
Confirmation of Normality of Statistical Distribution |
|
Items related to the second hypothesis |
0.13 |
0.24 |
Confirmation of Normality of Statistical Distribution |
|
Items related to the third hypothesis |
0.09 |
0.29 |
Confirmation of Normality of Statistical Distribution |
|
Items related to the forth hypothesis |
0.04 |
0.29 |
Confirmation of Normality of Statistical Distribution |
According to the results, the data is normally distributed.
In this section, according to the nature of research variables, the research hypotheses were tested using one-sample T test.
The t test method examines the hypothesis of the community's mean location. This test may be performed in such a way as to first assume the mean of society. Then, determine whether this framed hypothesis is correct or not by t test. This test can also be used to compare the mean of a sample with a constant number or claim. After formulating the hypothesis zero and vice versa, this test includes the following steps:
1- Calculation of t for collected data.
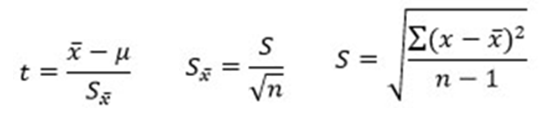
2. Calculating the freedom degrees using formula df = n-1
3- Determine the confidence level or the significance level
4. Referring to T tables that exist in different reference and extract the table t
5. Comparison the calculated t and table t
6. Deciding whether to reject or confirm the zero hypothesis
The questionnaire consisted of 22 questions that were designed to examine the factors affecting customers’ decision making in the sportswear industry based on a marketing mix model in Tehran City.
Five-point Likert scale has been used to design this section, which is one of the most commonly used measurement scales. Therefore, we compare the obtained mean with 3 to examine the hypotheses. The overall form and scoring of this scale for the questions is as follows:
Table2. The questionnaire score points based on Likert scale
|
Overview |
Very low |
low |
average |
high |
Very high |
|
Scoring |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
Results of The Research Hypotheses
Examining the first hypothesis : The product attributes affects the customers’ decision to purchase sportswear in Tehran City.
Investigating the effect coefficient of element of the product on the purchasing decision of sportswear customers in Tehran City indicates that this coefficient is estimated to be 0.15. Considering the value of the partial index (p-value) which is equal to P <0.01, as well as the significant number which is 1.07 and is less than 0.05 and less than 1.96, it can be concluded that this path coefficient is not significant at the error level of 0/05. That is, the product element does not affect the purchasing decision of sportswear customers in Tehran City. The significant effect of this hypothesis was rejected. Table 4 shows the results of this hypothesis review.
Table4. The path coefficients of the relationship of the first hypothesis
|
Hypothesis |
path coefficient |
p-value |
Significance number |
Result of test |
|
First |
0.15 |
P<0.01 |
1.07 |
Rejected |
Examining the second hypothesis : The price offered affects the customers’ decision to purchase sportswear in Tehran City.
Investigating the effect coefficient of the price offered on the purchasing decision of sportswear customers in Tehran City indicates that this coefficient is estimated to be 0.03. Considering the value of the partial index (p-value) which is equal to P <0.01, as well as the significant number which is 0.14 and is greater than 0.05 and less than 1.96, it can be concluded that this path coefficient is not significant at the error level of 0/05. That is, the price offered does not affect the purchasing decision of sportswear customers in Tehran City. The significant effect of this hypothesis was rejected. Table 5 shows the results of this hypothesis review.
Table5. The path coefficients of the second hypothesis
|
Hypothesis |
path coefficient |
p-value |
Significance number |
Result of test |
|
First |
0.03 |
P<0.01 |
0.14 |
Rejected |
Examining the third hypothesis: The place of supply and distribution of goods affects the customers’ decision to purchase sportswear in Tehran City.
Investigating the effect of the place of supply and distribution of goods on the purchasing decision of sportswear customers in Tehran City indicates that the path coefficient is estimated to be 0.12. Considering the value of the partial index (p-value) which is equal to P <0.01, as well as the significant number which is 0.86 and is greater than 0.05 and less than 1.96, it can be concluded that this path coefficient is not significant at the error level of 0/05. That is, the place of supply and distribution of goods does not affect the purchasing decision of sportswear customers in Tehran City. The significant effect of this hypothesis was rejected. Table 6 shows the results of this hypothesis review.
Table6. The path coefficients of the third hypothesis
|
Hypothesis |
path coefficient |
p-value |
Significance number |
Result of test |
|
First |
0.12 |
P<0.01 |
0.86 |
Rejected |
Examining the forth hypothesis : The advertisements affects the customers’ decision to purchase sportswear in Tehran City.
Investigating the effect of the advertisements on the purchasing decision of sportswear customers in Tehran City indicates that the path coefficient is estimated to be 0.12. Considering the value of the partial index (p-value) which is equal to P <0.01, as well as the significant number which is 5.01 and is greater than 0.05 and less than 1.96, it can be concluded that this path coefficient is significant at the error level of 0/05. That is, the advertisements level affects the purchasing decision of sportswear customers in Tehran City. The significant effect of this hypothesis was rejected. Table 7 shows the results of this hypothesis review.
Table7. The path coefficients of the forth hypothesis
|
Hypothesis |
path coefficient |
p-value |
Significance number |
Result of test |
|
First |
0.03 |
P<0.01 |
5.01 |
approved |
According to the analysis made, the research hypotheses are summarized in the table below:
Table8. Examining the research hypotheses
|
Row |
Hypothesis |
Result |
|
First |
The element of the product affects the customers’ decision to purchase sportswear in Tehran City. |
Rejected |
|
Second |
The price offered affects the customers’ decision to purchase sportswear in Tehran City. |
Rejected |
|
Third |
The place of supply and distribution of goods affects the customers’ decision to purchase sportswear in Tehran City. |
Rejected |
|
Forth |
The advertisements affect the customers’ decision to purchase sportswear in Tehran City. |
Approved |
According to the explanations, it is concluded that only advertisements affect the customers’ decision to purchase sportswear in Tehran City and companies and stores should spend on using the advertisement creativities.
Each paper has some limitations. The limitations of the present research are summarized in the following:
- It was very rigorous to obtain information on the subject of research and also, the researchers have found it difficult to use the resources and books related to the study.
- Unavailability of library resources in the subject of study.
- The lack of cooperation and familiarity from the side of respondents in the method of gathering information through questionnaire was the limitation. However the researcher tried his best to make them familiar and comfortable with questionnaire to collect better and complete answers from them.
- Finally, the lack of confidence in the answers provided by the respondents is one of the limitations of the present research.
1. Nezami, P. The Reviewing the Impact of Marketing Mix on Brand Equity (Case Study: ETKA Stores). Journal of Novel Applied Sciences Available online at www.jnasci.org. JNAS Journal-2013, 2(10): 517-521.
2. Raj, A, Arokiasamy, A.The Effect of Marketing Mix and Customer Perception on Brand Loyalty.Journal of Business and Management.2012, 4, 2: 1-11.
3. Keller, K. L. Building, Measuring, and Managing Brand Equity, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi. 2003:54-58.
4. Atilgan, E. Aksoy, S. &Akinci, S. Determinants of the brand equity: A verification approach in the beverage industry in Turkey. Marketing Intelligence & Planning. 2005, 23(3): 237-248.
5. JalaliFarahani M. (2013), The Effect of Selected Marketing Elements on Brand Value in Sport Services. Applied Research in Sport Management. 2 (6): 11-20
6. Iranzadeh S. Ranjbar A. Poursadegh N. (2012), Investigating the effect of marketing mix on brand equity. New Marketing Quarterly. 2 (3): 155-172
7. Sehat S. BajmalouyRostami H. Koshkooli M. (2012), Effect of Marketing Blend on the Value of the Brand Name of the Entrepreneur Insurance Company. Faculty of Management, University of Tehran.Commercial Management. (12): 71-90