|
Pushpa Yadav Research Scholar Faculty of Commerce Banaras Hindu University Varanasi, India, 221005 Contact No.- 9451602248 Email:Pushpa.phd0210@gmail.com |
Priyanka Gite Professor Faculty of Commerce Banaras Hindu University Varanasi, India, 221005 Contact No.- 07800559386 Email: cgite.priyanka@rediffmail.com |
Human Resource holds strategic position in the present era. The experience, knowledge and skills possessed by the employees are the real capital, especially for the knowledge based industry indeed banking industry. It is the main determinant for the productivity, profitability and sustainability, and forms basis for decision making to the investors all over the world. Disclosure of such an important element of the organization is important for information asymmetry. Considering the importance of Banking Industry in Indian economy and the importance of HR and HR Disclosure in this sector, the research paper aims to study present position of HR Disclosure Practices prevailing in Indian Banking Sector, and comparison of HR Disclosure Practices of Public, Private and Foreign Commercial Banks in India. It comprises study of 11 prominent commercial banks of India.
Keywords- Human Resource, Commercial Banks, Disclosure Practice, Disclosure Variables
Since liberalization the Indian economy is experiencing rapid changes in the business environment. Open economy and the growing capital market has given opportunities to global investors. Demand for financial reporting and disclosure arises from information asymmetry and agency conflicts between managers, outside investors, and intermediaries (Kothari, Xi & Short 2009). Reports or Disclosures act as medium of communication between the investors and the managers. Reports contain a set of quantified financial information about the performance, profitability and sustainability of the enterprise. The process of such communication with the outside world to facilitate investment decision is called Disclosure. The growing cut throat competition in every phase of business has shifted the valuation base from tangible to intangible assets of the companies. Intangible asset of the company is skill, expertise and technology it posses. Human resource is the prominent element of the Intellectual Capital.
Human Resources are the energies, skills, talents and knowledge of people which are, or which potentially can be applied to the production of goods or rendering useful services (Syed, 2009 ). It is fixed input which enables a firm to perform a particular task (Rubin 1973).
In the new economic setup intellectual and human capital are identified as major determinant of organizational value over other physical capital. The knowledge, skill and experience possessed by a person are defined as human capital. Investments in firm-specific HR practices such as training in firm-specific skills, on-the-job experience, coaching and mentoring can qualitatively differentiate a firm’s employees from those of other firms and can make Human Capital less imitable (Huselid, 1995). Human Resource being considered as strategic capital, its accounting and reporting aspects are becoming crucial for the organizational success (Imtiaz & Suman 2010).
Specially, for service industries like banks, insurance companies, software, call centers, consultancies, etc, these intangible are its real capital. Banks play an important role in the nation building process. Banking industries are also commercial entities engaged in financial intermediation by pooling the surplus and channelizing the savings to the deficit sector (Kainth & Agnihotri). The disclosure practices in the Indian Banking Sector are governed by the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 and RBI. Though there are complete set of provisions for the financial disclosures, non-financial disclosures are still voluntary. Realizing the importance of the non-financial disclosures, RBI is encouraging the banks to adopt non-financial disclosures apart from their financial disclosures (Chakrabarty, 2011). In the changing time, management of risk and human resource has emerged as two key challenges faced by the banking sector. Management of risk is possible only with an efficient and skilled manpower. Banking industry being a service industry, human resources are its most profitable asset. Thus Human Resource Disclosures is essential for a better insight in the profitability, sustainability and performance of the concerned bank and the economy as a whole.
The concept of human resource valuation was introduced by Flamholtz (1960) as a part of goodwill, which was followed by a series of researches on Human Resource, its validity and valuation in the enterprises. Further Conner L. (1991) in resource theory identified Human Resource or Personnel as ‘specific assets’ of the enterprise, having interdependent knowledge influencing the productivity. Sveiby (1997) advocated that since the HR are acquired by the organizations with a view to generate future revenues thus, HR must be considered as Capital and expenses on them should be capitalized while computing the value of the organization instead of treating them as expenses. According to Jaggi and Lau(1974) The stock market analysts feel that human resource accounting is an investor friendly disclosure as well as assuring the various stakeholders that the business has the right human asset to meet future requirement. On the other hand Subhash (2008) identifies the idiosyncrasies of individuals’ knowledge, skills and capabilities, HRM practices and organizational culture as constituents of Human Capital, which convey information to the capital market. Lee and Siddiq (2012), reveals that HR disclosure it has an impact on the decisions of the investors, clients and potential staff of the organization. Ulrich, Geller& Desouza(1984) discovered a positive correlation between HR Disclosure Practice and business Performance. Michel (2013) did not find any significant difference in the Nigerian financial and manufacturing companies. He identified was the lack of legislation for human resource disclosure as one of the reason for inadequate HR disclosure practice. Sharma & Kumar (2014) finds that the HR disclosure practice of public sector banks better than the private sector banks in India. Based on the importance of HR Disclosure Practices and the Commercial Banks in economy, the present study identifies the present state of HR Disclosure practice in present time.
The objectives of the study are as follows:-
1. To study the degree of HRD (Human Resource Disclosure) by the commercial banks in India.
2. To compare the disclosure practices of public, private and foreign commercial banks in India
The research hypothesis is-
H0: There is no significant difference in the Human Resource disclosure practices of public, private and foreign commercial banks in India.
H1: There is significant difference in the Human Resource disclosure practices of public, private and foreign commercial banks in India.
1. Sample Selection- Judgment sampling procedure has been applied to select the banks for the study. The banks enlisted in NSE being representative of the Indian commercial banking system has been considered as the examined for the study. Total 12 banks are enlisted in the ind_cnxbanklist which includes Public Sector, Private Sector and Foreign Banks. Since, IndusInd Bank Ltd. recently merged with Kotak Mahindra is excluded from the study making 11 banks under study as shown in Table 1.
Table 1: List of Banks listed in NSE classified on the basis of its ownership.
| S. No. | PUBLIC SECTOR BANKS | PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS | FOREIGN BANKS |
| 1. | State Bank of India | Axis Bank Ltd. | Federal Bank Ltd. |
| 2. | Bank of Baroda | HDFC Bank Ltd. | |
| 3. | Bank of India | ICICI Bank Ltd. | |
| 4. | Canara Bank | Kotak Mahindra Bank Ltd. | |
| 5. | Punjab National Bank | Yes Bank Ltd. |
Source: - ind_cnx bank index from www.nseindia.com
2. Source of Data- the study is empirical in nature and is based on secondary data source. Various sources of like, prospectus, press release, newspapers, magazines, etc. is used by the management to disclose the information and performance of their Banks. Despite of these, annual report is recognized as the most important source containing basic information of company. Based on the recent trends few Indian Commercial Banks are also publishing Business Responsibility Report as to disclose the Corporate Social Responsibility Report. Human Resource Disclosure is the prominent element in this report. Thus published annual report and business responsibility reports are collected from the websites of the banks for the study.
3. Period of the Study- the study examines the annual report and business responsibility report published by the banks for the financial year 2013-14.
4. Analysis of Data- Content Analysis is used to examine the disclosure practices of the commercial banks in India. Content analysis involved reading the annual report of each bank and coding the information contained therein in accordance with a selected framework (Guthrie and Petty, 2000). Major human resource disclosure has been identified from the previous study and a set of 19 major variables, (as shown in Table 2) is constructed as check list for the analysis.
Table 2: - Disclosure Variables Used For Study
| 1. | Separate HR Sheet |
| 2. | No. Of Employees |
| 3. | HR Policy |
| 4. | Mgmt Succession Plan |
| 5. | Employees Value Creation |
| 6. | Employment Report |
| 7. | Hr Development Fund |
| 8. | Employees / Worker's Fund |
| 9. | Training &Development |
| 10. | Employees Categories |
| 11. | Managerial Remuneration |
| 12. | Retirement Benefits |
| 13. | Award/Achievements |
| 14. | Performance Recognisition |
| 15. | Information On Welfare Of Employees |
| 16. | Pension Fund |
| 17. | Total Value Of HR |
| 18. | Superannuation Fund |
| 19. | Employee's Benefits |
Dichotomous procedure to score each bank’s index is used i.e. “1” was awarded if the variable is disclosed and “0” if the variable is not disclosed. After scoring each bank for all the variables, total disclosure score is calculated. HRDI is calculated for every bank to rank them accordingly. And descriptive Statistics is used to measure the level of HR disclosure practice prevailing in the Indian Commercial Banking Sector.
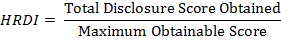
The commercial banks are categorized into 3 heads based on its ownership as, public sector banks, private sector banks and foreign banks. The list of which is given in Table 2. One way ANOVA is used to compare the disclosure practices of public, private and foreign commercial banks in India.
The study includes 11 commercial banks enlisted in NSE, which contains 5 public sectors, 5 private sectors and 1 foreign bank. The HR Disclosure is not governed by any legislation and is totally voluntary for the banks. ‘Training & Development’ variable ranked first among the other variables achieving 100% disclosure across the banks. This was followed by ‘number of employee’ variable. ‘Total Value of HR’ variable is the least disclosed variables by all the banks. This was followed by ‘Human Resource Development Fund’ gaining 9.09% (only disclosed by SBI) and ‘Superannuation Fund’ Scoring 18.18% of disclosure percentage.
Table 3: - Percentage of disclosure across disclosure variables
| S. No | Disclosure Variables | Total Disclosure | % of Disclosure |
| 1 | Separate HR Sheet | 8 | 72.7 |
| 2 | No. Of Employees | 10 | 90.9 |
| 3 | HR Policy | 4 | 36.4 |
| 4 | Mgmt Succession Plan | 5 | 45.5 |
| 5 | Employees Value Creation | 3 | 27.3 |
| 6 | Employment Report | 8 | 72.7 |
| 7 | HR Development Fund | 1 | 9.1 |
| 8 | Employees / Worker's Fund | 5 | 45.5 |
| 9 | Training &Development | 11 | 100.0 |
| 10 | Employees Categories | 8 | 72.7 |
| 11 | Managerial Remuneration | 8 | 72.7 |
| 12 | Retirement Benefits | 4 | 36.4 |
| 13 | Award/Achievements | 9 | 81.8 |
| 14 | Performance Recognisition | 5 | 45.5 |
| 15 | Information On Welfare Of Employees | 6 | 54.5 |
| 16 | Pension Fund | 10 | 90.9 |
| 17 | Total Value of HR | 0 | 0.0 |
| 18 | Superannuation Fund | 2 | 18.2 |
| 19 | Employee's Benefits | 9 | 81.8 |
The study and comparison of the disclosure practices of the individual banks is done with HRDI and the banks are ranked from highest to lowest scorer.
Table 4: - Human Resource Disclosure across Commercial Banks
| Name of Bank | Total Disclosure | HRDI | Rank |
| Bank Of Baroda | 15 | 75 | 1 |
| Bank of India | 14 | 70 | 2 |
| Punjab National Bank | 11 | 55 | 3 |
| ICICI Bank Ltd. | 11 | 55 | 3 |
| Kotak Mahindra Bank Ltd. | 11 | 55 | 3 |
| State Bank of India | 10 | 50 | 4 |
| YES Bank Ltd. | 10 | 50 | 4 |
| Axis Bank Ltd. | 9 | 45 | 5 |
| Federal Bank Ltd. | 9 | 45 | 6 |
| Canara Bank | 8 | 40 | 7 |
| HDFC Bank Ltd. | 8 | 40 | 7 |
Bank of Baroda scoring 75 HRDI ranks first among the banks. The total 15 variables out of 19 were disclosed in the bank’s annual report and business responsibility report. Canara Bank and HDFC Bank Ltd. with lowest HRDI 40, are ranked 7th i.e. among the banks under study, these banks have disclosed least information about their HR.
| Table 5: - Descriptive Statistics | ||||||
| N | Minimum Statistics | Maximum statistics | Mean statistics | Std. Deviation | Variance statistics | |
| Disclosure Variables (N) | 11 | 40.00 | 75.00 | 52.7273 | 11.26136 | 126.81 |
The descriptive test statistics with mean 52.72 depicts that moderate level of the HR disclosure practice prevails in the Indian commercial banking sector. The variance statistics of the sector scores 126.81 with minimum and maximum statistics being 40 and 75 respectively. This implies that wide level of variation in the HR disclosure practice prevails in the Commercial Banking Sector of India.
| Table 6:- SUMMARY | ||||
| Groups | Count | Sum | Average | Variance |
| Public Sector Banks | 19 | 11.6 | 0.610526 | 0.104327 |
| Private Sector Banks | 19 | 9.8 | 0.515789 | 0.125848 |
| Foreign Banks | 19 | 9 | 0.473684 | 0.263158 |
| ANOVA | ||||||
| Source of Variation | SS | d.f. | MS | F | P-value | F critical |
| Between Groups | 2.669856459 | 10 | 0.266985646 | 1.08 | 0.379244236 | 1.878766638 |
| Within Groups | 48.94736842 | 198 | 0.247208931 | |||
| Total | 51.61722488 | 208 | ||||
To compare the disclosure practices of public, private and foreign commercial banks in India One-Way ANOVA is used. In the test Since F<F Critical, at 5% level of significance, null hypothesis is accepted, i.e. there is no significant difference in the Human Resource disclosure practice of public, private and foreign commercial banks in India. The test also verifies that Foreign Banks have relatively greater variation in the HR Disclosure Practice as compared to Public and Private Banks. But the difference between them is not found significant.
Human Resource has always been a prominent resource in the organization. Even various technological advancement increasing inventions and innovations in the growing time period is unable to replace the role of human being in the organization. The emergence of knowledge based industry has magnified the importance of workforce. In the era of cut throat competition it is sought as a tool for competitive advantage. Thus the disclosure of this eminent capital of the organization is important for the investors and other decision makers associated to the organization. Commercial Bank is major service industry and the base of the economy. So, the paper aims to study the present position of HR Disclosure Practice prevailing in the Indian Commercial Banks. The study reveals HR Disclosure Practice is in its initial stage and is completely voluntary. Moderate level of HR Disclosure Practice prevails in the Indian Commercial Banks. A non-financial disclosures practice is yet to cover a long way to become a prominent part of the bank’s balance sheet. Indian Commercial Banks initiative for such practice is commendable, yet there is long way to go. Proper legislation is also required to promote unity in the disclosures.
The present study also has some limitations. The study is conducted on annual report and business responsibility report, yet different banks may have used other reports for the disclosure. The study is based on the reports of only one year, thus it does not reveals the trend and the progress in the HR Disclosure Practices of Indian Commercial Banks. These limitations can be used as basis for further research.