|
Vaibhav Misra M.Phil Scholar School for Management Studies Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University (A Central University) Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India Email: vaibhav.misra@aol.in |
The study is conducted on 179 respondents in the age bracket of 15 years to 35 years of Lucknow city with the purpose to investigate the impact of cultural factors over generation Y consumer decision making. The structured questionnaire stating the cultural factors on 3 point scale (1= agree, 2= can’t say and 3= disagree) was constructed keeping in mind the objective of the study and all other important aspects. Convenience sampling is used for collecting the data from the respondents. The property and nature of data is tested to making decision about use of correct statistical test. It is found that there is impact of cultural factors over generation Y consumer decision making.
Keywords- Culture, Imperatives, Consumer Preferences, Indian Market, Cultural Elements
Everybody in this world is a consumer. Every day of our life we are buying and consuming an incredible variety of goods and services. However, we all have different tastes, likes and dislikes and adopt different behavior patterns while making purchase decisions. Many factors affect how we, as individuals and as societies, live, buy, and consume. External influences such as culture, ethnicity, and social class influence how individual consumers buy and use products.
India has multi-cultured societies with many faiths, beliefs, (dogmatic as well as orthodox), varying geographical conditions and natural resources. Here culture is given very much importance. Culture affects the consumer to a great extent.
According to Liang (2009), the people born in the bracket of 1978 to 1995 are considered as generation Y (gen Y)
Culture is defined as apparent (extrovert) behavior of a society based on inherent or acquired mind set, beliefs and faith. Religion, geographical location, natural resources, social fabric, education and economic strength influence it. Apparently culture is thinking, living and working pattern of society. Culture includes all that man has acquired in his individual and social life and inherited from family and society. Culture is envisaged by Malinowski (1944) as “the handwork of man and as the medium through which he achieves his ends” Mathew Arnold’s (1988) words, culture is “the study of perfection and of harmonious perfection; general perfection and perfection which consists in becoming something, rather than in having something, in an inward condition of the mind and spirit, not in an outward set of circumstances” Dutch Management Professor Geert Hofstede (1997) refers to culture as the “software of the mind” and argues that it provides a guide for humans on how to think and behave; it is a problem solving tool.
Culture is the part of the external influences, which impact the consumer. There exists a complex relationship between culture and consumption pattern. Since culture is dynamic, it changes. The reason for the cultural changes can be identified as follows: acculturation, diffusion, revitalizing movements, technological development modernization impact of media etc. Consumer acculturation is a socialization process in which an immigrant or marginalized consumer learns the behaviors, attitudes and values of culture that are different from those of their culture of origin (Lee, 1988). Ogden et. Al. (2004) presents a review of the relationship between culture, specifically what has been termed ethnicity and its impact on consumer purchase decisions. Literature in anthropology and sociology focuses on the group factor of acculturation such as relationship to socialization, social interaction and mobility (Olmedo: 1979). The psychology literature emphasizes individual characteristics such as change in perception, attitudes, values and personality (Berry, 1980). Sociological studies favor theories of linear assimilation first outlined by Park (1950) who posits a process that is “Progressive and irreversible” based on stages of contact and culminates in the complete adjustment of the new entrant to the dominant culture. Based on his seminal studies of immigration to America, Gordon argues that all of the categories of identity create through historical circumstances, sense of group identity- of people hood. Several researchers have adopted a sociological perspective in consumer acculturation literature. Specifically the three groups displayed differences in reference group influence, media influence and store attribute importance and the patterns depended on the level of acculturation. Hagen and Bernett (1953) say that innovation leads to endogenous changes in cultural pattern. The impact of western culture can be very well observed on our youths. They are tempted by the western life style. It has been observed by the marketers hence they try to influence them through media.
Religion
Religion is considered to be most important element of culture. The author focused it as the element for study. The religion varies from person to person and from place to place. Every religion had different values and norms that affect the shopping behavior of the customers belonging to that particular religion.
Language
Language is also an important element of culture. Language varies from place to place. Language is considered as the major element cultural advertising; this is the main tool for creating the awareness of the product among the customers. Language helps the customers to understand the attributes and use of the product. Therefore it influences the purchasing behavior of the customers of any country. The major language used in UK for communication is English.
Cultural Values
Values also are beliefs. Values differ from other beliefs, how-ever, because they meet the following criteria:
Therefore, in a broad sense, both values and beliefs are mental images that affect a wide range of specific attitudes which, in turn, influence the way a person is likely to respond in a specific situation.
Beliefs
Beliefs consist of very large number of mental and verbal statements (for example: “I believe…..”) that reflects a person‟s particular knowledge and assessment of something (another person, a store, a product, a brand). (Schiffman & Kanuk, 1997)
Symbols
Symbols are words, gestures and pictures or objects that hold a particular meaning only recognizable by those who share the culture. This category includes words in a language or jargon, as well as dress codes, hairstyles, flags. New symbols can be developed and old ones disappear. (Schiffman & Kanuk, 1997)
Color
Color is considered as the important element of culture. For example- Saffron is the holy color of Hindus where as Muslims prefer green as holy color; when customers prefer to purchase the garments they consider color as an important factor of influencing their decision. (www.alibaba.com)
Objectives of the Study
The study is done to analyze how culture affects the preferences of Indian Consumers when purchasing the product. The study is based on following objectives:
The study is based on primary data which was collected from the shopping malls of Lucknow city. The respondents were targeted from the Saharaganj, East End Mall and Fun Mall. The profile of the respondents was selected on the basis of respondent’s age and gender. The questionnaire was designed keeping in mind the objectives and other important aspects of the study.
Sampling Method and Sample Size
The market for sampling was selected on the basis of cultural diversity. Convenience sampling technique was used to collect the data from the respondents. The sample size identified for the study using the following formula of infinite population. The calculation of sample size is represented below:
………………….. (i)
The total sample size determined for the study is 384 from targeted areas of Lucknow.
Data Collection
To collect the primary data structured questionnaire was distributed to 384 representatives of the target population. The responses received towards the distributed questionnaire are 179 respondents out of the determined sample size of 384 from the mentioned area of study the remaining respondents did not replied against the questionnaire. The secondary data is collected through the magazines, journals, periodicals, people opinion and internet.
Analytical Tools and Techniques Employed
The normality of the data is tested using Kolmogorov-Smirnov test and Shapiro-Wilk test of normality and homogeneity of the variance is tested using levene statistic. It is found that the data is normally distributed and homogenous but the data for some factors is non homogeneous in nature. Therefore, the test used in the study is ANOVA and Kruskal Wallis. The detail about the test is mentioned below:
Table 1: Information on Use of Statistical Test
| Property of Data | Nature of Data | Statistical Test | |
| Does Religion have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | Normally Distributed | Homogeneous | ANOVA |
| Does Traditions have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | Normally Distributed | Non Homogeneous | Kruskal-Wallis |
| Does Values have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | Normally Distributed | Homogeneous | ANOVA |
| Does Beliefs have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | Normally Distributed | Non Homogeneous | Kruskal- Wallis |
| Does Symbols have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | Normally Distributed | Non Homogeneous | Kruskal- Wallis |
| Does Colours have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | Normally Distributed | Non Homogeneous | Kruskal- Wallis |
Hypotheses of the Study
H0 There is no impact of cultural factors over generation Y consumer decision making.
Ha There is impact of cultural factors over generation Y consumer decision making.
The findings of my study are:
Table 2: Age Group
| Frequency | Percentage | |
| 15 Years to 20 Years | 47 | 26.3 |
| 20 Years to 25 Years | 56 | 31.3 |
| 25 Years to 30 Years | 46 | 25.7 |
| 30 Years to 35 Years | 30 | 16.8 |
| Total | 179 | 100.0 |
The age of the respondents were categorized in different age group starting from 15 years to 35 years. The categorized age groups are shown in Table 2. It is found that majority of respondents fall in the category of 20 years to 25 years of age group, followed by the respondents in the age group of 15 years to 20 years with the number of respondents of 56 and 47 respectively. 46 respondents are in the age group of 25 years to 30 years and 30 respondents are in the age group of 30 years to 35 years.
Chart 1: Age Group
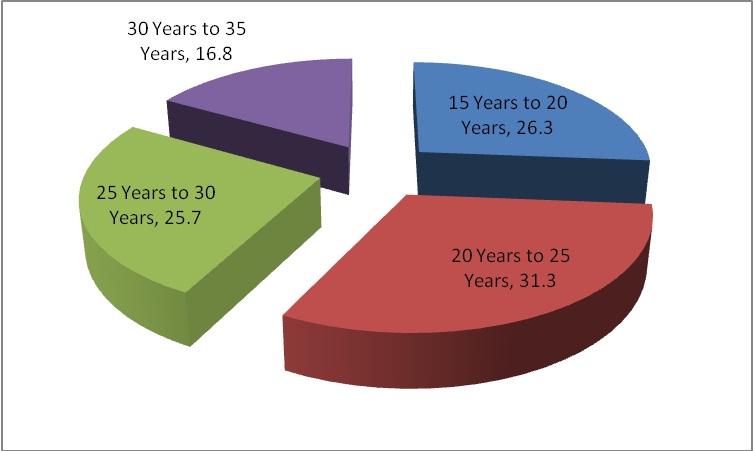
Chart 1 demonstrates the division of age group of the respodents, I found that the maximum respondents falls in the age group of 20 years to 25 years with 31.3% followed by the age group of 15 years to 20 years with 26.3%. It is also found that 25.7% of the respondents falls in the age group of 25 years to 30 years and 16.8% of the respondents are in the age group of 30 years to 35 years.
Table 3: Gender of the Respondents
| Frequency | Percentage | |
| Male | 92 | 51.4 |
| Female | 87 | 48.6 |
| Total | 179 | 100.0 |
Table 3, represents the gender division of the respondents, it is found that the number of male respondents is 92 and the number of female respondents is 87. Therefore it is found that male responded to the survey more as compared to female respondents.
Chart 2: Gender of the Respondents
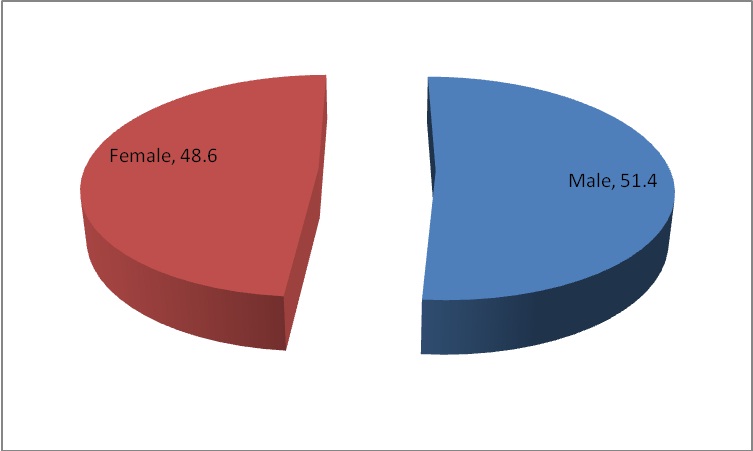
Chart 2, represents the pie chart stating the percentage of respondents in each gender category. It is found that 51.4% of the respondents are male and 48.6% of the respondents are female. Therefore it is found that male responded to the survey more as compared to female respondents.
Table 4: Educational Qualification of the Respondents
| Frequency | Percentage | |
| Below Graduate | 37 | 20.7 |
| Graduate | 30 | 16.8 |
| Post Graduate | 50 | 27.9 |
| Professionals | 44 | 24.5 |
| Others | 18 | 10.1 |
| Total | 179 | 100.0 |
Table 4 represents the educational qualification of the respondents; it is found that maximum numbers of the respondents are in Post Graduate with 50 respondents, followed by 44 respondents who are Professionals, 37 respondents are below Graduate, 30 respondents are Graduate and 18 respondents have educational qualification which is not mentioned in the questionnaire.
Chart 3: Educational Qualification of the Respondents
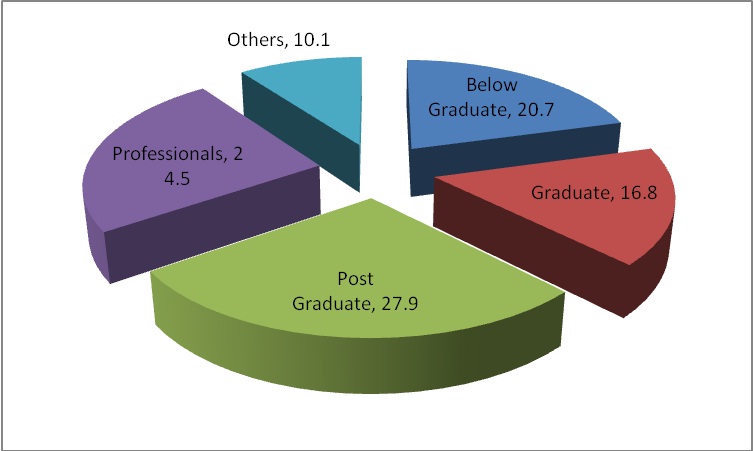
Chart 3, represents the educational qualification of the respondents, 27.9% of the respondents are Post Graduate, 24.5% of the respondents are Professionals, 20.7% of the respondents are Below Graduate, 16.8% of the respondents are Graduate and 10.1% of the respondents have the educational qualification that is not mentioned in the questionnaire.
Table 5: Does Culture have any impact over generation Y consumer decision making?
| Frequency | Percentage | |
| Yes | 63 | 35.2 |
| No | 116 | 64.8 |
| Total | 179 | 100.0 |
Table 5 represents the view of the respondents concerning the impact of the culture over consumer decision making, it is found that 116 respondents answered that culture does not have any impact over consumer decision making.
Chart 4: Does Culture have any impact over generation Y consumer decision making?
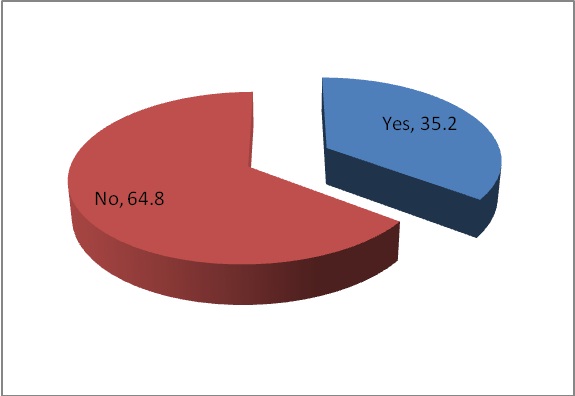
Chart 4 represents the pie chart stating the view of consumers towards the impact of cultural factors over generation Y consumer decision making. It is found that 64.8% of the respondents answered that there is no impact of cultural factors over generation Y consumer decision making. 35.2% of the respondents answered that there is impact of cultural factors over generation Y consumer decision making.
Table 6: Test of Normality
| S.No | Property of Data | |
| 1 | Does Religion have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | Normally Distributed |
| 2 | Does Traditions have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | Normally Distributed |
| 3 | Does Values have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | Normally Distributed |
| 4 | Does Beliefs have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | Normally Distributed |
| 5 | Does Symbols have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | Normally Distributed |
| 6 | Does Colours have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | Normally Distributed |
The normality of the data is tested using Kolmogorov-Smirnov test and Shapiro-Wilk test of normality a shown in Table 6. It is found that the data is normally distributed.
Table 7: Test of Homogeneity of the Variance
| S.No | Nature of Data | |
| 1 | Does Religion have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | Homogeneous |
| 2 | Does Traditions have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | Non Homogeneous |
| 3 | Does Values have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | Homogeneous |
| 4 | Does Beliefs have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | Non Homogeneous |
| 5 | Does Symbols have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | Non Homogeneous |
| 6 | Does Colours have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | Non Homogeneous |
Table 7 checks the homogeneity of variance Levene Statistic is used in the study. This statistic will indicate about the nature of the data or in other words this statistic will inform whether the data is homogeneous of non-homogeneous. The test is performed on the basis of median. It is found that the data related to religion and values are homogeneous in nature; whereas, the data related to the traditions, beliefs, symbols and colors is non homogeneous in nature.
Table 8: Test of Reliability
| Cronbach’s Alpha | No. of items |
| .984 | 6 |
Table 8 represents the reliability statistics of the questionnaire with the help of Cronbach’s Alpha, as suggested by Sweet & Grace-Martin (2008), any value above .70 is considered to be reliable and consistent. As the value of Cronbach’s Alpha is .984 which is very high from the Sweet & Grace-Martin, (2008) suggested value of .70. Therefore, it is analyzed that the questionnaire is reliable and consistent.
H0 There is no impact of culture over consumer decision making.
Ha There is impact of culture over consumer decision making.
To test the hypothesis developed for the study both ANOVA and Kruskal-Wallis tests are used. The results for the significance of the same are represented in Table 9 and 10 respectively.
Table 9: ANOVA
| Sig. | |
| Does Religion have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | .000 |
| Does Values have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | .000 |
Table 9 represents the test of ANOVA over two factors namely religion and values. The questions related to religion and values are considered dependent variable and the question does culture have any impact over consumer decision making is considered as independent variable. It is found that there is effect of religion and values over consumer decision making. The results are highly significant at 1% level of significance.
Table 10: Kruskal- Wallis Test
| Asymp. Sig. | |
| Does Traditions have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | .000 |
| Does Beliefs have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | .000 |
| Does Symbols have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | .000 |
| Does Colours have effect over Consumer Decision Making? | .000 |
Grouping Variable: Does Culture have any impact over consumer decision making
Table 10 represents the Kruskal- Wallis test over four factors namely traditions, beliefs, symbols and colours. The questions related to traditions, beliefs, symbols and colours are considered dependent variable and the question does culture have any impact over consumer decision making is considered as grouping variable. It is found that there is effect of traditions, beliefs, symbols and colours over consumer decision making. The results are highly significant at 1% level of significance.
Therefore, based on the analysis null hypothesis- there is no impact of culture over consumer decision making is rejected and alternative hypothesis- there is impact of culture over consumer decision making is accepted.
The purpose of my study was to investigate the impact of cultural factors over consumer decision making. My study concludes that the factors religion, traditions, values, beliefs, symbols and colour have impact over consumer decision making.
My study also found that there is significant impact of cultural factors over consumer decision making.
The culture of India varies from the region to region as India is culturally diversified country. Therefore, the marketers are suggested to understand the culture of the consumers before penetrating the product in Indian market. This is possible that one product may get the success in one region and may not be successful in other region due to cultural diversification.